Exploring Painful Testicle and Groin Symptoms

Intro
Pain in the testicles and groin regions often brings a slew of unsettling feelings. Many individuals, both young and old, may brush off such discomfort until it escalates. However, it's essential to understand the myriad causes underlying these symptoms. Knowledge here is power; it equips individuals to identify issues early and seek appropriate care when needed.
Research Context
Background Information
Painful testicle and groin symptoms are more than mere inconveniences; they can signal serious health issues. Conditions range from common ailments such as epididymitis to more severe issues like testicular torsion. The groin pain often further complicates diagnoses, involving various intertwined systems in the body.
Importance of the Study
Given that these symptoms can dramatically impact daily life—affecting everything from work to intimacy—this study aims to shed light on their causes, diagnostic techniques, and management strategies. Understanding these aspects can empower individuals to approach their health proactively and with informed awareness.
Discussion
Interpretation of Results
Through the examination of various studies and clinical insights, it's clear that numerous factors can contribute to pain in the testicle and groin region. Injury during sports or physical activities is quite common—often dismissed as "nothing serious." However, overlooked injuries could lead to chronic pain or complications if left untreated.
Once in clinical settings, providers typically run through a variety of diagnostic tests, including ultrasounds and urinalysis, to better understand the underlying causes. Generally, they must differentiate between infections, trauma, or more severe conditions. This diagnostic process not only provides clarity but also informs treatment strategies moving forward.
Comparison with Previous Research
Past research has largely focused on specific conditions related to painful testicles and groin. In many cases, studies have found that patients often delay seeking treatment due to embarrassment or lack of immediate symptoms. The prevailing wisdom suggests that awareness and communication regarding these issues can lead to faster diagnosis and treatment. This conclusion has emerged more prominently in light of recent findings that link prompt medical consultation to better long-term outcomes.
In summary, knowledge surrounding painful testicle and groin symptoms is not merely academic; it holds tangible implications for everyday living. Recognizing the signs and understanding the potential issues can significantly influence one’s health journey.
Foreword to Painful Testicle and Groin Symptoms
Pain in the testicle and groin isn't something most folks like to chat about, but it’s crucial to understand this topic for various reasons. First off, ignoring such symptoms can lead to more than just discomfort; it can pose significant health risks. Understanding the potential causes and treatment options can empower individuals to take charge of their health more effectively.
When examining painful symptoms in these regions, it's essential to recognize how interconnected the body is. Pain felt in one area can often relate to issues in another, making accurate diagnosis a bit of a puzzle. Moreover, these symptoms can significantly affect one’s quality of life, impacting everything from personal relationships to daily actions. Thus, clarity on this topic can be enlightening for many, including students, researchers, and medical practitioners.
Definition and Overview
Painful testicle and groin symptoms can manifest through various sensations, such as aching, sharp stabbing pains, or a dull throb, often accompanied by swelling or redness. This pain can stem from multiple underlying issues, ranging from benign conditions to serious health emergencies like testicular torsion or tumors. A comprehensive understanding of what these symptoms entail aids in facilitating timely medical interventions. This overview serves as a springboard into deeper discussions surrounding specific causes, the nature of pain experienced, and how to manage such challenges effectively.
Prevalence of Painful Testicle and Groin Symptoms
Although it might seem that these are rare occurrences, painful symptoms in the testicle and groin are surprisingly common. According to various studies, approximately 1 in 5 men will experience significant pain in these areas at some point in their lives. This condition does not discriminate, affecting individuals at different ages and activity levels. Factors such as physical activity, lifestyle choices, and underlying health conditions all contribute to the prevalence and nature of the pain experienced. The likelihood of encountering this issue makes awareness crucial.
In summary, being in the know about painful testicle and groin symptoms can lead to better health outcomes. By educating themselves, individuals can make informed decisions about when to seek medical help, ultimately alleviating the strain such pain can bring.
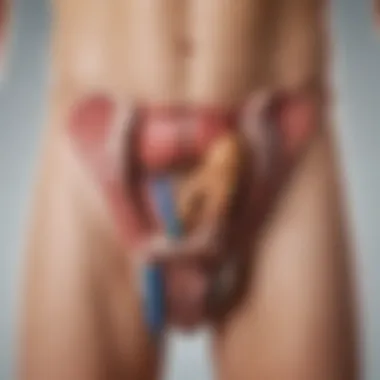
Anatomy of the Groin and Testicular Region
Understanding the anatomy of the groin and testicular region is paramount in grasping the full scope of painful symptoms that may arise in these areas. This knowledge lays the groundwork for discerning various conditions, from minor irritations to serious health threats. Familiarity with the anatomical layout also aids both patients and healthcare providers in effective communication regarding symptoms and concerns. Additionally, recognizing the structures involved helps in pinpointing the exact source of discomfort, which can ultimately influence diagnosis and treatment plans.
Key Structures Involved
The groin area, also known as the inguinal region, encompasses several critical anatomical components that work in harmony but can also be sources of discomfort when affected by injury or illness. Here are the main components:
- Testes: These oval-shaped organs reside within the scrotum, producing sperm and hormones such as testosterone. Any discomfort or swelling can indicate an underlying issue.
- Epididymis: This coiled structure sits atop the testes and is responsible for storing and maturing sperm. It’s not uncommon for inflammation here to cause pain.
- Spermatic Cord: This vital structure contains blood vessels, nerves, and the vas deferens, connecting the testes to the pelvic cavity. Twisting of the spermatic cord is referred to as testicular torsion, a critical emergency.
- Inguinal Canal: A passage through which the spermatic cord travels. Inguinal hernias can occur when tissue pushes through a weak spot in this area, leading to pain.
- Ligaments: Various ligaments support the scrotum and pelvis, and any strain or injury can result in significant discomfort.
While most people are familiar with the testes, many may not realize the importance of connected structures, which can create a cascade of issues when something goes awry.
"Knowing what’s where in the groin and testicular region can make a world of difference in diagnosing pain correctly."
Nerve Pathways and Pain Sensation
Pain in the groin can be complex, not only due to the varied structures involved but also because of the nerve pathways that transmit pain signals. The key nerves to consider include:
- Ilioinguinal Nerve: This nerve supplies sensation to the skin of the groin as well as the inner thigh. Irritation or injury here can lead to localized pain.
- Genitofemoral Nerve: It separates into two branches, one of which serves the scrotum. This nerve is crucial in providing sensory feedback.
- Pudendal Nerve: Responsible for the sensation in the perineal area, it can also refer pain from pelvis conditions to the groin.
When we experience pain, our body interprets signals sent through these nerves. Discomfort may originate from the groin but may manifest differently based on nerve involvement. For example, nerve irritation caused by inflammation or enlarged tissue can escalate the sensation of pain, leading to significant distress even when there is no direct injury to the groin region itself. This interconnected pain pathway complicates diagnosing and managing groin and testicular discomfort.
In summary, grasping the anatomy of the groin and testicular region is essential for understanding the potential causes of pain. A detailed comprehension of the structures involved and how nerve pathways operate prepares the ground for better diagnosis and treatment of these complex symptoms.
Common Causes of Pain in the Testicle and Groin
Understanding the various common causes that can lead to pain in the testicular and groin regions is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Pain can arise from a variety of issues – some relatively benign while others may require urgent medical attention. Identifying these causes helps people take appropriate action and prevents small issues from escalating into significant health problems. Additionally, recognizing the symptoms associated with these causes can empower individuals to seek medical advice swiftly, ensuring any underlying conditions are addressed.
Injury and Trauma
Sports-related Injuries
dive into sports-related injuries, which can be a notable factor contributing to groin and testicle pain, especially among active individuals. Whether it's a sudden impact during a game of football or an awkward landing after a jump in basketball, these injuries can cause strain or trauma to the surrounding structures. A key characteristic of sports-related injuries is their often sudden nature, leaving athletes and enthusiasts no time to brace for impact.
While these injuries are common, they can lead to more severe problems if left unattended. For instance, a strain can sometimes result in a tear, leading to swelling and prolonged pain. Understanding sports-related injuries in the context of this article helps underline the need for proper warmup routines and strength training, which are essential to minimize risk.
Accidents or Falls
Accidents or falls present another significant cause of testicular and groin pain. A fender bender, misstep on a staircase, or simply tripping on the sidewalk can unexpectedly lead to injury in these sensitive areas. The crucial aspect of accidents is that they often come about without warning, which heightens the risk of serious injury.
A unique feature of this cause is the broad range of incidents that can result in pain. Sometimes it may be a mild bruise, while other times, it could be something serious like a fracture or a deep tissue injury. This variability underscores the importance of remaining vigilant about minor injuries that might seem trivial at first but can complicate over time.
Infections and Inflammation
Epididymitis
Epididymitis is a prevalent cause of testicular pain, marked by inflammation of the epididymis, the coiled tube at the back of the testicle responsible for sperm storage. What makes epididymitis noteworthy in this article is its commonality. It can often develop due to infections, trauma, or the effects of urinary tract issues.
A distinguishing factor about epididymitis is that it often presents with additional symptoms beyond just pain. Patients may also experience swelling, tenderness, and sometimes fever. Getting to grips with this condition's nuances can assist individuals in seeking appropriate treatment in a timely manner.
Orchitis


Orchitis, an inflammation of one or both testicles, frequently occurs alongside epididymitis. The significance of this condition stems from its potential to affect fertility and can stem from viral or bacterial infections, including the mumps virus. Orchitis stands out in the discussion due to its serious risk factors; when due to viral infections, it can lead to complications that might not resolve without specific treatment.
Patients suffering from orchitis often describe a heavy sensation in the affected testicle, which hastens them to seek medical advice. This article benefits from examining orchitis because it emphasizes the need for awareness of viral risks and the importance of vaccinations, such as the MMR vaccine, in preventing mumps-related complications.
Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections bear a profound connection to groin and testicular pain as they can lead to discomfort that radiates to these areas. They occur more commonly in women but should not be overlooked in men, as they can lead to significant complications, including prostatitis. A fundamental characteristic of urinary tract infections is their ability to cause burning sensations during urination alongside potential pain in the lower abdomen and flank.
A unique feature in this context is the potential overlap of symptoms with other conditions, making it vital for individuals to discuss any unusual pains with healthcare providers. Understanding urinary tract infections enhances the article’s depth, highlighting how something seemingly simple could herald more complicated health issues if not addressed correctly.
Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion is another critical cause of testicular pain that merits considerable attention. It occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. This sudden onset of severe pain typically requires immediate surgical intervention to salvage the affected testicle. The importance of recognizing testicular torsion lies in its urgency; if the condition isn't addressed swiftly, it can lead to loss of the testicle, making diagnosis and treatment crucial.
In summary, a spectrum of causes ranging from injuries to infections, and including conditions like testicular torsion, contribute to painful testicle and groin symptoms. By garnering awareness of these causes, individuals can take informed steps toward better health and prompt medical intervention, aligning with the article's overarching goal.
Uncommon and Serious Conditions
Understanding uncommon and serious conditions related to painful testicle and groin symptoms is crucial. While some cases arise from common ailments, others can indicate more severe health issues. Discerning these conditions can mean the difference between effective management and dire consequences. This section shines a light on less common presentations that require careful attention.
Hernias
Hernias are notably significant as they might be mistaken for less alarming conditions. They occur when an internal part of the body pushes through a weakness in the muscle or surrounding tissue wall.
Inguinal Hernias
Inguinal hernias are one of the frequent types encountered. They happen when fatty tissue or a part of the intestine protrudes through a weak spot in the abdominal muscles, often noticeable in the groin. A key characteristic of inguinal hernias is the presence of a noticeable bulge in the groin or scrotum, particularly when standing up or straining.
This condition is a relevant consideration because the risk of complications like strangulation, where the blood supply to the intestines gets cut off, looms if not addressed promptly. Unique to inguinal hernias is their tendency to affect men more than women, primarily due to anatomical differences. If undiagnosed, they can disrupt daily activities, causing long-term problems.
Femoral Hernias
Femoral hernias, in contrast, occur lower in the groin, typically affecting women more than men. Here, tissue bulges through a weak spot in the femoral canal, which contains the femoral vein and artery. A hallmark of femoral hernias is that they may cause acute discomfort in the inner thigh or groin and can also lead to serious complications.
They matter in this discussion due to their higher likelihood of incarceration and strangulation. While they are less common than inguinal hernias, vigilance is crucial, as symptoms could escalate swiftly. Femoral hernias often necessitate surgical intervention, especially when pain and discomfort surface.
Tumors and Cancers
The possibility of tumors and cancers represents a serious aspect that cannot be overlooked. These conditions might initially present as benign but can have profound implications.
Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer stands out as a notable concern due to its prevalence among younger men. This cancer often manifests as a lump or swelling in the testicle, which may be painless initially. What makes it remarkable is how early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes.
The ability to identify changes early empowers individuals in managing their health. A unique feature is the psychological impact; men are often reluctant to seek help due to embarrassment or fear. However, increasing awareness and educating patients is essential for addressing testicular cancer effectively.
Lymphatic System Involvement
Another critical area is the involvement of the lymphatic system, as it can indicate metastasis from other primary sites. Lymph node swelling can occur in the groin region, reflecting underlying systemic issues. The key characteristic here is that it often ties to more severe forms of cancer.
This aspect is uniquely significant because it highlights the extensive reach of various cancers beyond just their origin. Understanding that pain in the groin may not always stem from local issues broadens the diagnostic scope for healthcare providers.
Referred Pain from Other Areas
Lastly, referred pain plays a vital role in recognizing sources of discomfort. It can mislead individuals into thinking they are experiencing local issues when, in actuality, the pain arises from distant organs.
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones can radiate pain towards the groin and testicles, often causing significant distress. The primary feature of kidney stones is acute, sharp pain, typically felt in the lower back or side, which travels down to the groin. Their relevance in discussions about groin pain lies in their nature; while sometimes the pain feels localized, the origin can be quite distant.
Unique to kidney stones is how they can provoke associated symptoms, such as nausea and hematuria, which provide valuable clues for diagnosis. Quick identification and management are crucial to prevent prolonged suffering.
Pelvic Issues
Pelvic issues, such as those resulting from endometriosis or other gynecological concerns, can also lead to groin pain. This type of referred pain often presents a diagnostic challenge due to overlapping symptoms. A notable characteristic is the potential for cyclical pain, coinciding with menstrual cycles in women.
Understanding pelvic issues in relation to groin pain emphasizes the need for integrated care, as effective management of symptoms often requires addressing both the reproductive and urinary systems. Recognizing these interconnectedness benefits both patients and practitioners, enhancing treatment approaches across disciplines.
Addressing uncommon and serious conditions effectively not only improves individual health outcomes but also enriches the understanding of complex pain pathways associated with the testicular and groin regions.
Signs and Symptoms to Monitor
Monitoring the signs and symptoms of painful testicle and groin conditions is crucial for a number of reasons. Being attuned to one’s body can lead to early detection and often better outcomes. Pain is rarely an isolated experience; rather, it tends to come with its companions—other symptoms that could signal either minor inconveniences or serious medical issues. Recognizing changes can guide individuals in seeking appropriate medical intervention.
Intensity and Duration of Pain
The intensity and duration of pain play a pivotal role in assessing the nature of the underlying condition. Acute pain that appears suddenly may indicate issues like testicular torsion or an injury, which require immediate evaluation by a healthcare professional. On the other hand, chronic pain that lingers could suggest something less urgent but equally concerning, such as chronic epididymitis.
Understanding the levels of pain can also shape treatment approaches. It helps clinicians determine whether an intervention is necessary or if pain management techniques, like over-the-counter medications or lifestyle adjustments, might suffice. As a general rule, if the pain feels debilitating or lasts longer than a few hours, it's wise to seek expert advice.
Associated Symptoms
Monitoring associated symptoms can help in pinpointing the underlying cause of groin and testicle pain. Here are a few crucial ones to keep a watch on:
Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea and vomiting often go hand in hand with many conditions affecting the testicular and groin region. These symptoms can indicate an underlying infection or a significant complication. For instance, if someone experiences these symptoms along with testicular pain, it may suggest an issue like a severe infection, and immediate care might be warranted. The notable feature of nausea is that it often reflects the body's response to pain or distress, making it an important sign for healthcare providers to consider.
The unique aspect of nausea and vomiting lies in their potential to escalate the overall discomfort. While they may appear to be secondary issues, they can point to more serious medical conditions. Therefore, acknowledging their presence when discussing symptoms with a healthcare practitioner is essential.
Fever
Fever is another key indicator to consider. It frequently suggests that the body is combating an infection or inflammation. In the context of painful testicle and groin symptoms, a fever may accompany conditions like epididymitis or orchitis. The characteristic of fever, in this case, is its role as a measurable sign of underlying pathology, informing the clinician that an active pathological process is at play.
Notably, the presence of fever can signify a more urgent medical issue that requires close monitoring and treatment. Thus, when experiencing fever associated with groin discomfort, it is crucial to seek medical care without delay.


Changes in Urination
Changes in urination—such as frequency, urgency, or pain during urination—might suggest complications related to urinary tract infections, kidney stones, or even prostate issues. The significance of changes in urination lies in its direct link to the urinary system and its interaction with the reproductive organs.
Physicians often utilize these changes as diagnostic markers during assessments. They can inform the clinician about the potential involvement of the urinary tract in conjunction with testicular or groin pain, helping to solidify the diagnosis. Being aware of such urinary changes can offer critical insights into the overall health status and should be discussed openly during medical consultations.
In summary, keeping an eye on the intensity and duration of pain, along with being mindful of various associated symptoms can be a game changer in diagnosing and managing testicle and groin conditions.
Diagnosis of Painful Testicle and Groin Symptoms
Diagnosing painful testicle and groin symptoms is a crucial step in finding the right treatment and alleviating discomfort. A comprehensive diagnosis not only identifies the root cause of pain but may also unearth underlying health issues that could manifest in various ways. With a structured approach, medical professionals can accurately pinpoint the underlying problem, which can range from minor injuries to more serious health conditions.
Having a clear understanding of the diagnostic process helps patients feel more at ease. It empowers them with knowledge, potentially easing the anxiety that accompanies unexplained pain. Moreover, recognizing the nuances involved in this process allows for prompt and appropriate treatment, which is paramount given that some conditions can worsen over time without intervention.
As part of the diagnostic approach, there are a few specific methods that stand out. The medical history and symptoms must be assessed with thoroughness. The physical examination techniques employed will also play a pivotal role. Finally, various diagnostic imaging methods offer crucial insights into the nature of the problem.
Medical History and Symptoms Assessment
When it comes to diagnosing painful testicle and groin symptoms, an individual's medical history serves as the bedrock of the process. This assessment includes details about previous illnesses, surgeries, and any medications currently taken. Each factor can provide insights that guide doctors towards the right direction.
Patients should be ready to discuss:
- Duration and intensity of the pain
- Any recent injuries or trauma
- Associated symptoms like nausea or fever
- Any history of infections
These conversations provide a roadmap for medical professionals, helping them determine if the pain is likely to stem from a musculoskeletal issue or a potential infection, thereby refining their examination strategy.
Physical Examination Techniques
Following the medical history assessment, the physical examination comes into play, enabling the healthcare provider to visually and physically assess the groin and testicular area. This examination can reveal signs of swelling, tenderness, or other abnormalities, which may indicate specific conditions.
Key techniques during the examination may include:
- Inguinal canal inspection to detect hernias
- Tenderness assessments of the testicles
- Evaluation of the scrotal sac size and consistency
The insights gained here are invaluable. They not only contribute to narrowing down the potential causes but also guide the subsequent decision on whether imaging or further tests are needed.
Diagnostic Imaging Methods
In the context of painful testicle and groin symptoms, diagnostic imaging methods like ultrasound and CT scans are vital in reinforcing findings from the physical examination and medical history. Both provide a more detailed view of the internal structures, helping to clarify the diagnosis further.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a primary tool in this diagnostic process. It is non-invasive and allows for real-time imaging of the testicles and surrounding tissue. One of the key characteristics of ultrasound is its ability to differentiate between solid masses and fluid-filled cysts. This capability is essential for ruling out testicular tumors or identifying conditions like epididymitis.
Unique features of ultrasound include:
- Real-time imaging: The ability to monitor changes as they happen.
- Non-radiative nature: Unlike X-rays, it does not expose patients to radiation, making it safer, especially for younger individuals.
The advantages of ultrasound encompass its speed and effectiveness in diagnostic assessments. However, it may have limitations when it comes to viewing deep abdominal structures, where a CT scan would be more beneficial.
CT Scans
CT scans provide a more comprehensive evaluation, especially for conditions that may involve organs beyond the immediate vicinity of the groin and testicles. One of its standout characteristics is its capacity to deliver high-resolution images of both soft tissue and bone.
Key benefits of CT scans include:
- Detailed cross-sectional images: These help in identifying issues that may not be visible through physical examinations alone.
- Broad area of evaluation: It can show potential issues in related structures, including the abdominal or pelvic organs.
Nonetheless, CT scans involve radiation exposure and sometimes require the use of contrast agents, which may not be suitable for all patients. Therefore, this method is usually reserved for more complex cases where ultrasound does not provide sufficient clarity.
A thorough understanding of the diagnostic process for painful testicle and groin symptoms is essential. This approach ensures a careful assessment that can lead to effective treatment and ultimately improve quality of life.
Management and Treatment Options
Management and treatment options for painful testicle and groin symptoms are crucial in addressing both acute and chronic pain effectively. Understanding how to manage these symptoms can significantly improve a person's quality of life, allowing them to return to their regular activities more comfortably. This approach encompasses various strategies, from immediate care for sudden pain through to long-term therapies aimed at chronic conditions. Choosing the right treatment depends on the underlying cause, severity of symptoms, and individual patient needs.
Immediate Care for Acute Pain
When experiencing sudden and intense pain, immediate care is critical. Proper management can alleviate discomfort and prevent complications from worsening conditions.
Pain Relief Strategies
Pain relief strategies play a pivotal role in managing acute testicular and groin pain. The basic idea is to reduce discomfort while addressing the underlying cause. Common strategies include the use of over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen or acetaminophen, which can help in lowering inflammation and bringing down pain levels.
The main characteristic of these strategies lies in their accessibility — they are widely available without prescription. The beneficial aspect is the quick action they provide, often leading to rapid pain relief for most individuals. However, one should be cautious when using medications, as long-term use can lead to side effects or other complications related to kidney or liver functions.
Rest and Ice Application
Resting and applying ice is another immediate care method for managing pain in the testicular area. This strategy focuses on reducing swelling and giving the body a chance to heal naturally. Just a simple ice pack wrapped in a cloth can work wonders. Leaning back with your legs elevated might also help in minimizing discomfort.
A key characteristic of this method is its simplicity and non-invasive nature. It effectively addresses pain without introducing additional medications into the system. It’s important to remember that while this technique offers immediate relief, it might not address the underlying cause, so following up with a medical evaluation is essential for persistent pain.
Long-term Management for Chronic Symptoms
Managing chronic symptoms requires a different approach, focusing on sustainable strategies that consider ongoing pain and its impact on daily life.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is a fundamental aspect of long-term management for chronic testicular and groin pain. It offers targeted exercises and manual therapies aimed at improving flexibility, strength, and overall function. Oftentimes, the pain associated with the groin area can stem from muscular or structural issues that are addressed through specialized stretches and exercises.
The uniqueness of physical therapy lies in its personalized nature; each treatment plan is tailored to the patient's specific needs. Not only does it help reduce pain, but it often leads to improved mobility and performance in daily activities. On the downside, physical therapy might require a significant time commitment and may take a while before visible results manifest, which can test the patience of some individuals.
Medications
Medications for chronic conditions might range from anti-inflammatory drugs to neuropathic pain medications. They serve to manage symptoms while also addressing underlying factors contributing to chronic discomfort. This approach can be both beneficial and complicated. While medications can offer relief, their effectiveness often varies from one individual to another.

One strong point about medications is their ability to manage pain on an ongoing basis, making daily life more tolerable. However, it’s crucial to strike a balance, as dependence on medications can lead to tolerance or potential side effects, thus necessitating regular consultation with healthcare providers for appropriate monitoring.
Surgical Interventions
For some individuals, surgery is the most definitive solution for pain in the testicular and groin areas, especially when conservative methods fail.
Repair of Hernias
Repairing hernias is often key in managing symptoms related to inguinal or femoral hernias. This often involves surgical techniques such as open repair or laparoscopic surgery. The objective is to fix the underlying issue that is causing pain by returning the tissue to its rightful place.
The main characteristic of hernia repair is its potentially immediate relief from symptoms post-surgery. Many patients report significant improvement in pain and functionality. However, there are risks involved with surgery, such as complications during the procedure or recovery time post-surgery.
Treatment of Testicular Torsion
Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency that requires immediate intervention to alleviate pain and save the affected testicle. Treatment typically involves untwisting the spermatic cord and securing the testicle to prevent recurrence.
The unique feature of this intervention is the urgency with which it must be acted upon. A timely surgical response can make a substantial difference in preserving testicular function. On the other hand, the invasive nature of surgery might bring about concerns regarding recovery and the possibility of post-operative complications.
Impact on Quality of Life
The experience of painful testicle and groin symptoms can significantly alter an individual’s day-to-day living. These pain episodes don’t just linger in the background; they can cause disruptions in both physical and emotional realms. Understanding this impact highlights the essential need for addressing the underlying causes and managing the symptoms effectively. A more tailored approach ensures not only the alleviation of pain but also the restoration of one’s quality of life.
Emotional and Psychological Effects
Chronic pain in the testicular and groin regions often does more than simply hurt—it leads to emotional and psychological struggles as well. The intricate link between physical discomfort and mental well-being is well-documented. Individuals experiencing persistent symptoms may find themselves battling feelings of anxiety, depression, and isolation.
- Anxiety: The uncertainty associated with recurrent pain might cause a lingering fear of potential underlying serious conditions. Patients may obsess over possible diagnoses, leading to increased anxiety that amplifies the experience of pain itself.
- Depression: When discomfort becomes a regular companion, it can even lead to significant mood changes. The joy in daily activities diminishes, creating a cycle where pain leads to a decrease in social interactions, further exacerbating depressive feelings.
- Isolation: Those suffering might withdraw from their social circles. The fear of embarrassing moments related to their symptoms might prevent them from engaging in social or recreational activities. This can result in a profound sense of loneliness that affects not only the individual but also their relationships.
Understanding these psychological consequences is crucial for developing effective treatment plans. Holistic management strategies should incorporate mental health support to address these challenging aspects.
"Pain is inevitable, but suffering is optional." This quote underscores the importance of managing both physical symptoms and emotional responses to achieve a better quality of life.
Physical Activity Limitations
Pain in the testicle and groin regions extends its influence into physical capabilities. The ability to partake in regular activities—be it sports, exercise, or even simple chores—might become compromised. This limitation can lead to a decreased physical fitness level, which can, in turn, impact overall health and well-being.
- Exercise Restrictions: High-impact activities, such as running or weightlifting, may become untenable. This might lead individuals to abandon their exercise regimes altogether, resulting in loss of stamina and muscle strength. Such changes can promote other health issues, like weight gain or cardiovascular problems.
- Work Impacts: Occupational activities might also suffer. If a job requires physical labor or even prolonged sitting, pain can hinder performance. Consequently, this may lead to increased sick days, lower productivity, and potential job insecurity.
- Recreational Limitations: On a personal level, individuals might miss out on recreational hobbies they once enjoyed. Whether it’s playing a pickup game of basketball or hiking, the desire to engage diminishes when pain becomes a constant factor.
In effect, the implications of painful testicle and groin symptoms reach far beyond mere discomfort; they create waves that ripple through every facet of a person's life. Addressing both emotional and physical impacts is integral in promoting an improved quality of life and encouraging individuals to seek timely intervention.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Understanding when to seek medical attention for painful testicle and groin symptoms is crucial. Patients often question what warrants a visit to a healthcare provider, and the ability to discern urgency can mean the difference between appropriate treatment and complications. Ignoring symptoms can lead to serious consequences, as many underlying issues require prompt intervention.
Recognizing the signs that should trigger a visit to the clinic or emergency room is essential in managing these symptoms effectively. From severe pain to associated systemic reactions, various red flags may indicate that the situation is dire.
Urgent Symptoms Indicating Serious Conditions
Several symptoms should not be brushed off when considering the severity of testicular and groin pain. The following are among the most concerning and warrant immediate medical evaluation:
- Sudden and Intense Pain: If there is a sudden onset of severe pain in the testicular area, it could suggest testicular torsion or a serious rupture.
- Swelling or Discoloration: Noticeable swelling or changes in color of the affected area may indicate significant injury or infection that needs urgent care.
- Nausea and Vomiting: These symptoms accompanying testicular pain can signal not just discomfort but underlying serious conditions like torsion or infection.
- High Fever: Fever, particularly when intense, often suggests an infection that could spread and cause further complications if not treated promptly.
- Changes in Urination: If you experience painful urination, blood in the urine, or a strong urgency with inability to void, these signs must be taken seriously.
> Staying alert to these symptoms can significantly affect outcomes. Early intervention is key in minimizing complications.
Regular Check-ups and Vigilance
Routine check-ups play an integral role in maintaining testicular and groin health. Men often neglect regular examinations, which can lead to late diagnosis of potentially serious conditions. A consistent schedule of medical evaluations not only promotes prevention but also enables early detection of issues before they escalate into emergencies.
- Annual Physical Exams: Aim for yearly check-ups with a primary care provider. These visits help establish baseline health metrics and facilitate discussions about any changes.
- Self-Examination: Learning how to perform a testicular self-exam is effective for identifying abnormalities. Regular self-checks can help catch issues while they are still manageable.
- Awareness of Symptoms: Being in-tune with one’s body is vital. If something feels off, it should never be dismissed. Communicate any persistent or worrying symptoms to your physician.
By emphasizing vigilance and preventative care, the likelihood of managing painful symptoms increases, thereby preserving quality of life and reducing the risk of serious health issues.
Preventive Measures and Health Education
Preventive measures play a crucial role in managing painful testicle and groin symptoms, as they not only help in early detection but also reduce the risk of developing serious conditions. Understanding how to prevent issues before they arise involves a combination of regular health practices and education. This section looks into basic strategies and resources that empower individuals to take charge of their health, ideally leading to timely interventions and enhanced overall well-being.
Basic Preventive Strategies
Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups are essential in maintaining reproductive health and catching potential issues early on. These appointments with healthcare providers allow for comprehensive evaluations where practitioners can identify any changes or abnormalities in the testicular and groin areas.
One key characteristic of regular check-ups is the proactive monitoring of health. It is not just about addressing issues when they arise but rather about fostering an environment where health is prioritized. This approach can lead to a more informed patient and hopefully prompt intervention before symptoms escalate into serious conditions.
The unique feature of these check-ups is their ability to establish a baseline of what is normal for an individual’s body. By regularly documenting one’s health status, healthcare providers can discern what changes might signal a problem. The advantages include earlier diagnosis and treatment, potentially alleviating more serious issues down the line.
Awareness of Symptoms
Awareness of symptoms serves as a first line of defense against developing complications. When individuals know what symptoms to look for—such as persistent pain, swelling, or changes in urinary patterns—they can act quickly and seek professional medical advice, which might prevent worsening conditions.
The key characteristic of awareness of symptoms is its emphasis on education. It empowers individuals to be vigilant and proactive regarding their health. As a common strategy, it has been shown to promote engagement in one’s health management, resulting in quicker response times when issues arise.
A unique aspect of this awareness is the sharing of knowledge within communities, often leading to increased social support. The advantages of maintaining symptom awareness include quick access to care and the potential for improved outcomes in case of serious underlying conditions.
Educational Resources for Patients
Informative Literature
Informative literature encompasses a range of resources, including pamphlets, articles, and brochures distributed by clinics, hospitals, or health organizations. This literature is aimed at educating individuals about painful testicle and groin symptoms, guiding them through the sea of information available.
A significant benefit of this literature is that it provides targeted information, often written in a digestible format, ensuring a broader understanding of complex topics. The key presence of clear guidance allows individuals to navigate their symptoms effectively and feel more prepared to engage in discussions with healthcare providers.
The unique feature of informative literature is its ability to supplement conversations with healthcare professionals. Rather than relying solely on verbal communication, individuals can refer to printed materials, enhancing retention of important information. However, one disadvantage could be the potential for misinformation if the literature is not from a credible source.
Support Groups
Support groups provide a platform where individuals experiencing similar symptoms can come together to share experiences and coping strategies. These groups, whether in-person or online, help foster a sense of community, reducing feelings of isolation that often accompany health challenges.
The primary characteristic of support groups is their community-driven approach. By connecting people, they create a supportive network that emphasizes mutual care and understanding. This can significantly enhance emotional resilience while navigating painful symptoms.
One advantage of support groups is the lived experience often shared within them, presenting real-life coping strategies. However, a potential drawback could be the variability in group quality and the level of support provided; not all groups may provide constructive or accurate information.
By understanding the intricate relationship between awareness, education, and proactive health measures, individuals can take informed steps towards safeguarding their well-being.















