Understanding Back Pain's Link to Heart Health

Intro
Back pain is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide. While often perceived as a musculoskeletal issue, recent research suggests a deeper connection with heart health. Understanding this connection can lead to better preventive measures and timely intervention. Many individuals may not realize that their back pain could indicate underlying heart conditions. This article aims to illuminate these associations, outlining how and when back pain might serve as a warning sign of heart health concerns.
The relationship between these two symptoms is complex and multifaceted. This article will explore various aspects, including physiological mechanisms that link back pain to heart issues, the significance of early medical evaluation, and common heart conditions associated with this type of pain. As we delve into these topics, the importance of recognizing risk factors and the implications of neglecting such signals will come into focus.
In this context, readers will gain valuable insights essential for their overall health management.
Prelude to Back Pain and Heart Health
Back pain and heart health are often viewed as separate health issues. However, they can be interconnected in ways that are critical to understand. Recognizing this connection is essential for timely diagnosis and treatment. Chronic back pain can sometimes serve as a warning sign for underlying heart conditions. Failure to recognize this link may lead to serious health complications.
Overview of Back Pain
Back pain is a common ailment that affects a wide range of individuals across different age groups. It can vary in intensity and duration. Some people experience sharp, acute pain, while others deal with a dull, persistent ache. The causes can be numerous, including muscle strain, herniated discs, arthritis, and even poor posture. Interestingly, research indicates that up to 80% of people will experience back pain at some point in their lives. This statistic underscores the relevance of understanding back pain, not only for its discomfort but also for its potential implications for overall health, including cardiovascular issues.
It is also important to note that the impact of back pain stretches beyond physical suffering. It can affect mental well-being, limiting daily activities and hindering quality of life. Identifying the source and nature of back pain is crucial in managing treatments effectively. Patients must be aware that their back pain could correlate with other, more severe health conditions.
The Heart: An Overview
The heart is an intricate organ, vital for sustaining life. It pumps blood throughout the body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste products. Understanding how the heart functions gives insight into potential issues that may arise, especially when symptoms like back pain emerge. The cardiovascular system is not just about the heart but also encompasses blood vessels and circulation. A problem in any part of this system can lead to complications.
Common heart-related conditions include coronary artery disease, heart attacks, and irregular heartbeats, all of which can have diverse symptoms. For instance, myocardial infarction may not only present with chest pain but can also manifest as discomfort in the back. This overlapping of symptoms necessitates a careful evaluation by healthcare professionals for accurate differentiation between musculoskeletal and cardiovascular issues.
Understanding the heart's mechanisms can aid in recognizing when back pain might be indicative of a more serious condition.
In summary, exploring the relationship between back pain and heart health allows for a better understanding of symptoms, risk factors, and necessary medical evaluations. This interconnectedness is vital for promoting awareness and timely intervention.
Physiological Link Between Back Pain and Heart Conditions
Understanding the physiological link between back pain and heart conditions is critical in health care. This link may not seem apparent initially, but various dynamics within the human body connect these two seemingly unrelated health issues. An awareness of this connection can lead to better patient outcomes and timely interventions.
In this section, we will explore how back pain may arise from heart diseases and how heart conditions themselves can manifest as back pain. Recognizing these relationships enables both individuals and health professionals to respond effectively to symptoms that could signify more severe health concerns.
Nerve Pathways and Pain Signals
The human body’s nervous system is complex. It comprises a network of nerves that send signals to and from the brain, indicating sensations such as pain. Back pain can originate from numerous conditions affecting the spine or muscular structure. Yet, heart issues can also create pain that is interpreted as originating from the back. This occurs due to overlapping nerve pathways.
Pain from heart conditions, like myocardial infarction, might travel along nerve pathways, ultimately leading the brain to misinterpret the source. For example, the thoracic spine region is closely linked to the heart, so pain signals can radiate back to the upper or mid-back when heart issues arise. This miscommunication can lead to delayed treatment, where patients treat back pain without recognizing a possibly serious heart condition.
Referred Pain Mechanisms
Referred pain is an essential concept to grasp when discussing back pain related to heart health. Referred pain happens when pain is perceived in an area different from its actual source. In the case of heart-related issues, the pain may manifest in areas such as the back, neck, or jaw, complicating the clinical picture.
In particular, conditions like angina pectoris can lead to sensations in the back, often mistaken for mechanical back issues. Recognizing these mechanisms is fundamental for timely diagnosis. Health providers should take a detailed patient history and inquire about pain patterns or other associated symptoms, such as shortness of breath, sweating, or nausea, which may accompany heart-related back pain.
"Pain is an intricate signal, and its origin may not always be where one expects it to be. Understanding referred pain helps in identifying conditions that might otherwise be overlooked."
The interplay between nerve pathways and pain patterns highlights the importance of comprehensive assessments in patients presenting with back pain. It is vital to consider heart health as a potential underlying cause in these scenarios to avoid missing critical interventions.
Conditions Associated with Back Pain and Heart Issues
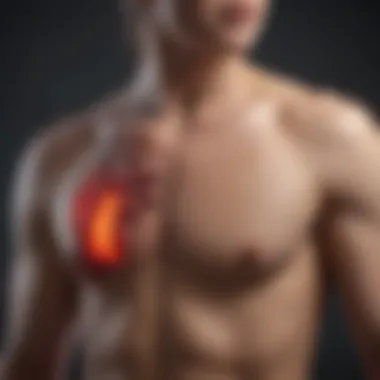

The interplay between back pain and various heart conditions holds significant relevance for both the medical community and patients. Recognizing this connection can lead to the early detection of serious cardiovascular problems. Often, patients may dismiss back pain as a mere musculoskeletal issue. However, in some cases, it can indicate underlying heart issues that require urgent attention. Thus, understanding these associations empowers individuals to seek medical evaluation when necessary. This awareness can potentially save lives.
Myocardial Infarction
Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, is one of the more severe conditions linked to back pain. Patients experiencing a heart attack may present symptoms that are not only chest pain but can also include discomfort radiating to the back. This scenario complicates diagnosis as many will attribute back pain to less serious issues.
Factors that contribute to myocardial infarction include:
- Coronary artery disease: This is the most common cause, where arteries become narrow, reducing blood flow to the heart.
- Risk factors: Factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, and sedentary lifestyle increase the likelihood of a heart attack occurring.
Recognizing signs early is crucial, as the faster one receives medical intervention, the better their chances of survival.
Angina Pectoris
Angina pectoris is another condition associated with back pain that signals inadequate blood flow to the heart. Patients may describe angina as a feeling of pressure or squeezing in the chest, which could extend to the back, neck, or arms.
It is helpful to understand the main triggers of angina:
- Physical exertion: Engaging in strenuous activities can provoke symptoms.
- Stress: Emotional stress and anxiety may also induce angina episodes.
- Cold weather: Changes in the environment often affect the frequency of angina attacks.
Angina can act as a warning signal for potential future heart events. It should not be ignored, as timely medical help can provide management options that improve life quality and longevity.
Aortic Dissection
Aortic dissection is a rare but life-threatening condition that can occur when the inner layer of the aorta tears. This can lead to severe back pain, often described as tearing or ripping. The pain typically spreads to other areas and can mimic other conditions.
Several factors increase the risk of aortic dissection:
- Hypertension: Chronic high blood pressure can weaken the aortic wall, making it more susceptible to tearing.
- Connective tissue disorders: Conditions like Marfan syndrome can predispose an individual to this issue.
- Age: The risk increases as one gets older. Most cases occur in individuals between 60 and 70 years.
Awareness of the symptoms of aortic dissection is critical, as this condition demands immediate medical attention. The consequences can be fatal without prompt treatment.
In summary, recognizing the association between back pain and these heart-related conditions is essential. Each condition presents unique symptoms and risk factors. Familiarity with these aspects enhances the ability to respond effectively to potential health crises.
Symptoms of Heart-Related Back Pain
Understanding the symptoms of heart-related back pain is crucial for timely medical intervention. While back pain is a common complaint, it can sometimes indicate more serious underlying heart conditions. Recognizing these symptoms can differentiate between a benign musculoskeletal issue and a potentially life-threatening heart problem. This section elaborates on the key symptoms to monitor, particularly the red flags that require immediate attention and the physical indicators that may signal a connection to heart health.
Identifying Red Flags
Red flags are warning signs that indicate a health issue may be more serious than originally thought. When it comes to back pain related to heart conditions, these symptoms should prompt an urgent medical evaluation:
- Sudden Onset of Severe Pain: A sudden and intense pain, especially if accompanied by other symptoms, should not be ignored.
- Chest Discomfort: Pain that radiates from the chest and travels to the back may indicate cardiac issues.
- Shortness of Breath: Difficulty breathing can be a sign that the heart is not functioning properly.
- Sweating and Nausea: Unexplained sweating or feeling nauseous alongside back pain can be alarming and suggest a heart attack.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling faint can signify inadequate blood flow to the brain, which could be related to cardiac issues.
Always consider these red flags seriously. If they occur, it’s essential to seek immediate care.
Physical Symptoms to Monitor
Monitoring specific physical symptoms can reveal important insights into the potential connection between back pain and heart health. Some symptoms to observe include:
- Pain Location: Notice if the pain is situated in the upper back or shoulders. This could relate to heart problems.
- Radiating Pain: Pay attention if pain spreads to arms, jaw, or neck. This suggests a more severe condition.
- Persistent Pain: Back pain that doesn’t resolve with typical treatments might warrant further investigation.
- Pain with Activity: If back pain worsens during physical exertion, this may highlight a heart issue.


Remember: Self-diagnosis is not advisable. These symptoms are not definitive and require professional assessment for accurate diagnosis.
Risk Factors That Elevate the Connection
Understanding the various risk factors that strengthen the relationship between back pain and heart health is crucial. These factors can help identify individuals who may be at increased risk for experiencing heart issues manifested as back pain. Factors like age, gender, and lifestyle play an essential role in this connection. Knowledge of these risk factors can lead to early intervention, better management of symptoms, and improved overall health outcomes.
Age and Gender Considerations
Age and gender significantly influence susceptibility to both back pain and heart conditions. Generally, older adults face higher risks for both issues due to the degeneration of muscles and tissues over time.
- Age:
As people age, the body undergoes various changes. Discs in the spine may lose hydration and elasticity, leading to back pain. Simultaneously, arteries can harden, increasing the risk of heart diseases. Understanding these changes allows for early monitoring and intervention. - Gender:
Men tend to develop heart issues earlier than women, while women may experience more pronounced back pain due to hormonal changes, especially during menopause. Recognizing these gender differences helps health professionals tailor preventive strategies according to specific needs.
For example, post-menopausal women are at a greater risk for osteoporosis, which can lead to back pain due to fractures.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle choices critically affect both back pain and heart health. Factors such as diet, physical activity, and stress management require attention for maintaining overall well-being.
- Physical Activity:
Sedentary lifestyle increases the likelihood of both back pain and heart issues. Regular exercise strengthens muscles, maintains spinal health, and supports cardiovascular functions. It is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week. - Diet:
A diet high in saturated fats, sugars, and refined grains may contribute to obesity, which is a known risk factor for heart disease and can exacerbate back pain. A balanced diet rich in whole foods, including fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats, promotes better overall health. - Stress Management:
Chronic stress can lead to muscle tension, particularly in the back, and increase blood pressure, negatively impacting heart health. Implementing stress-reduction techniques such as mindfulness, yoga, or breathing exercises can help mitigate these risks.
By recognizing and addressing these lifestyle factors, individuals not only improve their back health but also support their hearts.
In summary, factors like age, gender, physical activity, diet, and stress management play a pivotal role in the link between back pain and heart conditions. Understanding these risks allows individuals to make informed choices, promoting prevention and fostering a better quality of life.
Diagnostic Procedures for Evaluation
In exploring the connection between back pain and heart health, diagnostic procedures play a crucial role. These evaluations help in identifying underlying issues that may link the two conditions. Timely and accurate diagnosis is essential. By recognizing the symptoms early, it can prevent severe complications and enhance overall health outcomes. A thorough assessment combines patient history, physical examinations, imaging techniques, and laboratory tests.
Clinical Assessment and History
The first step in the diagnostic process involves a detailed clinical assessment. During this phase, healthcare professionals analyze the patient's medical history. They ask about the nature of the back pain, its duration, and any other symptoms, particularly those related to the heart. This history-taking process is valuable. It allows the doctor to spot patterns or red flags that may indicate a heart issue, such as radiating pain, shortness of breath, or unusual fatigue.
Equally, understanding the patient’s risk factors is vital. Conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease can significantly influence the evaluation. Thus, integrating personal and familial health information is critical for reaching an accurate diagnosis.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging is often necessary to shed light on the internal structures related to back pain and possible heart conditions. Common imaging techniques include X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans. Each method offers distinct insights:
- X-rays provide a basic overview of bone structure and can identify fractures or abnormalities in the spine.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is more detailed. It can visualize soft tissues, including discs, nerves, and even the heart to some extent.
- Computed Tomography (CT) scans combine multiple X-ray images to produce cross-sectional views of the body, showing detailed bone structures and potential tumors.
Being aware of the precise reasons to utilize these techniques can lead to prompt and effective treatments. Early intervention through accurate imaging can help differentiate between musculoskeletal issues and more serious cardiac concerns.
Blood Tests and Biomarkers
Blood tests are an essential component of the diagnostic landscape. They help in measuring various biomarkers that may indicate heart problems. For example, tests for cardiac troponins are common. Elevated levels can signify heart muscle injury, potentially tied to back pain caused by cardiovascular issues.
Other tests may include:
- Lipid panel: Assesses cholesterol levels, which can be linked to heart disease risk.
- Complete blood count (CBC): Helps identify infections or other underlying health issues.
- Basic metabolic panel: Evaluates organ function and electrolyte balance, which can influence heart health.
These blood tests provide vital information, complementing the clinical and imaging evaluations, to form a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health status.


Management Strategies for Heart-Related Back Pain
Addressing heart-related back pain requires immediate and long-term strategies that can significantly impact overall health. This section discusses the necessity of effective management strategies that are aimed not just at alleviating pain, but also ensuring that any underlying heart conditions are properly evaluated and treated. Correct management can prevent complications and improve the quality of life.
Immediate Response and Care
When a patient presents with back pain, the first step is to assess the severity and nature of the pain. Immediate care involves several critical actions:
- Assess Vital Signs: Monitoring blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate can provide important clues about possible cardiac issues.
- Pain Location: Determine if the pain is localized to the back or if it radiates to other areas such as the chest, shoulders, or arms. This helps establish if the pain is potentially heart-related.
- Emergency Care: If there are signs of a heart attack, such as sharp chest pain, shortness of breath, or sweating, emergency medical services should be contacted immediately.
"Back pain can sometimes serve as a precursor to serious heart conditions. Recognizing the signs early can be life-saving."
Post-assessment, the focus should shift to pain management options that do not mask symptoms but instead provide genuine relief. Ice packs or heat may be beneficial, depending on the nature of the pain. Access to immediate medical intervention is crucial if symptoms suggest potential heart problems.
Long-Term Management Approaches
Long-term management of heart-related back pain involves a multi-faceted approach:
- Physical Therapy: A tailored exercise regime can strengthen core muscles, promoting better posture and potentially alleviating pain.
- Medications: Pain relief can be managed with NSAIDs or other prescribed medications, but these should be used judiciously and under medical guidance.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation greatly benefit overall cardiovascular health and can mitigate back pain.
- Regular Monitoring: Engaging in regular health screenings can help track heart health parameters and detect any emerging conditions early on.
- Psychological Support: Chronic pain can affect mental health. Psychological counseling or support groups can assist individuals in coping with both pain management and any anxiety related to potential heart issues.
Implementing these strategies fosters a proactive approach to health, facilitating the necessary adjustments that an individual may need to live free of pain while keeping heart health front and center. Regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure that any emerging issues are promptly addressed.
Preventive Measures for Heart Health
Preventive measures for heart health play a crucial role in the context of back pain. Maintaining heart health is imperative not only for overall well-being but also for mitigating risks associated with conditions that may manifest through back pain. By understanding this relationship, individuals can take proactive steps that may significantly reduce their vulnerability to severe health issues.
Lifestyle Modifications
Implementing lifestyle modifications can have a profound impact on heart health. It is essential to focus on habits that promote cardiovascular wellness. These changes can also alleviate back pain when applicable.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity, especially aerobic exercises, strengthens heart muscles and enhances circulation. It can help maintain a healthy weight, which is crucial since obesity is a risk factor for both heart problems and back pain. Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent choices.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can promote heart health. Foods high in omega-3 fatty acids, like salmon, and fiber can help reduce inflammation, which is beneficial for both heart conditions and back pain.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Smoking is a leading factor in heart disease. It is equally detrimental to spinal health, as it can decrease blood flow and oxygen to the vertebrae. Quitting smoking significantly improves both heart and back conditions.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can exacerbate both heart disease and back pain. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be effective in managing stress levels. Finding ways to unwind can result in a healthier heart and a less tense body generally.
Regular Health Screenings
Regular health screenings are critical for early detection and management of potential heart conditions. Routine evaluations allow for tracking risk factors such as hypertension, cholesterol levels, and diabetes.
- Blood Pressure Check: Hypertension is often dubbed the 'silent killer.' Monitoring blood pressure can help in managing it effectively, reducing the risk for heart-related issues that may connect to back pain.
- Cholesterol Tests: Knowing your cholesterol numbers provides insight into heart disease risk. Elevated cholesterol levels can lead to atherosclerosis, which can indirectly cause back pain through diabetes and other complications.
- Blood Sugar Levels: High blood sugar can lead to chronic conditions that affect overall health. Monitoring glucose levels can help prevent diabetes, which is associated with both heart and back conditions.
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals enable individuals to stay informed about their health. > "Prevention is more effective than treatment. Early intervention can save lives and enhance the quality of life."
Ending: Awareness and Action
The significance of awareness and timely action cannot be overstated when addressing the connection between back pain and heart health. In this article, we explored various aspects that highlight how back pain can often indicate underlying heart conditions. Recognizing this potential link serves as a critical step in proactive healthcare management.
Early intervention has proven to be crucial in preventing complications related to heart conditions. Ignoring persistent or unusual back pain might lead to missed diagnoses of serious health issues such as myocardial infarction or angina pectoris. By fostering a culture of awareness, individuals can seek timely evaluations and avoid detrimental health outcomes.
The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention plays a pivotal role in enhancing treatment outcomes. When individuals seek medical help promptly upon experiencing back pain, health professionals can conduct necessary assessments without delay. Here are several key benefits of early intervention:
- Prevention of Complications: Detecting heart issues at an early stage can prevent more complex health problems.
- Informed Treatment Options: Early diagnosis offers a wider array of treatment options, allowing for tailored approaches to individual needs.
- Reduction of Anxiety: Knowing the cause of back pain alleviates worry about undiagnosed conditions, promoting mental well-being.
- Improvement of Quality of Life: Effective management leads to an overall enhancement in lifestyle and reduces discomfort associated with both back pain and heart conditions.
Empowering Individuals with Knowledge
Knowledge is empowerment. The more informed an individual is about the interplay between back pain and heart health, the better prepared they are to take action. Educating oneself about symptoms, risk factors, and available medical evaluations promotes proactive health management. Here are some strategies to enhance knowledge:
- Stay Informed: Regularly read articles and research studies on cardiovascular health.
- Engage in Community Discussions: Online platforms, such as Reddit or health forums, can provide insights from others' experiences.
- Consult Professionals: Regular discussions with healthcare providers about changes in health can yield valuable information.
- Utilize Resources: Websites like en.wikipedia.org and britannica.com offer extensive information on related health topics.
"Awareness is the first step towards action."















