Melanoma In Situ Surgery: A Comprehensive Overview
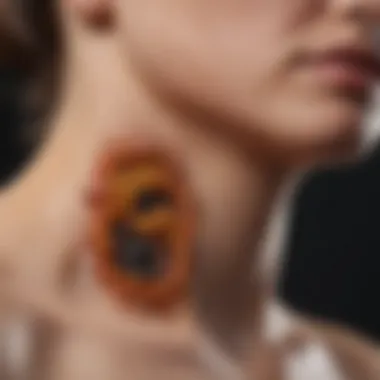

Intro
Melanoma in situ stands as a crucial point in the dermatological landscape, representing an early and impactful stage of skin cancer. A fundamental understanding of this condition is vital for both patients and healthcare professionals. This article aims to shed light on various surgical interventions involved in treating melanoma in situ, together with the comprehensive post-operative care required for optimal recovery and long-term results.
Research Context
Background Information
Melanoma in situ is defined as a non-invasive form of melanoma, localized to the epidermis. This condition typically arises from the uncontrolled proliferation of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin. Its management primarily involves surgical excision, which aims to completely remove the cancerous tissue while sparing healthy skin.
Various studies suggest that early detection and intervention can significantly reduce the risk of progression to invasive melanoma, underlining the importance of timely surgical treatment.
Importance of the Study
This article is significant because it explores a multitude of factors surrounding surgical practices for melanoma in situ. With the incidence of skin cancer rising globally, it is imperative to equip medical professionals and patients with the necessary knowledge and tools for informed decision-making. Understanding surgical techniques, associated risks, and post-operative care strategies is not just beneficial—it is essential in ensuring better outcomes for those affected.
"The key to effective treatment is not only in the surgery itself but also in comprehending the entire care process that follows."
Discussion
Interpretation of Results
As we delve into the surgical methodologies available for melanoma in situ, it is clear that the choice of technique can vary based on factors such as the thickness of the melanoma, its location, and the patient’s overall health. The traditional surgical excision remains a primary approach; however, newer techniques like Mohs micrographic surgery offer a high cure rate with maximized preservation of surrounding healthy tissue.
One must also consider the psychological impact of a melanoma diagnosis. Comprehensive care plans that address these emotional aspects can enhance recovery and provide support in navigating the surgical journey.
Comparison with Previous Research
Previous research widely supports the efficacy of early surgical interventions in improving survival rates and minimizing recurrence. For instance, studies published in journals such as The Journal of Clinical Oncology outline that cases treated promptly have significantly better prognoses than those left untreated for extended periods. The alignment of this newer evidence with past findings validates current surgical practices while encouraging ongoing research into optimization and innovation in the treatment of melanoma in situ.
By synthesizing insights from both contemporary and historical contexts, we arm ourselves with a rich understanding of melanoma in situ surgery, fostering an informed approach to future patient management.
Understanding Melanoma In Situ
Understanding melanoma in situ is crucial for those engaged in the realm of skin cancer. This particular condition is an early stage of melanoma, where the cancer cells remain confined to the outermost layer of the skin, known as the epidermis. The significance of recognizing this stage cannot be overstated. At this point, melanoma has not yet invaded deeper skin layers or metastasized to other organs. This characteristic affords a unique opportunity for early intervention, which can drastically improve surgical outcomes and minimize the potential for progression.
Definition and Characteristics
Melanoma in situ can be defined as a localized form of melanoma characterized by atypical melanocytes within the epidermis. These abnormal cells display a range of morphological changes, which can include irregular shapes and sizes. In most cases, this condition may appear as a flat lesion that varies in color, often exhibiting shades of brown, black, or even red. It is essential to differentiate melanoma in situ from more advanced stages, where invasive characteristics emerge.
Some key characteristics of melanoma in situ include:
- Asymmetry: The shape of the mole is irregular.
- Border: The edges are jagged or notched, rather than smooth.
- Color: The pigment is not uniform and can show varying shades.
- Diameter: Lesions larger than 6 millimeters should raise suspicion.
- Evolving: Any changes in size, shape, or color warrant medical evaluation.
A clinical examination is often the first step in identifying such lesions. Dermatologists rely on a combination of visual inspection and dermatoscopic evaluation to assess the nature of skin lesions.
Pathophysiology of Melanoma
The pathophysiology of melanoma in situ involves the transformation of normal melanocytes into malignant cells. This transformation can be attributed to several factors. Genetic mutations play a significant role, particularly those induced by ultraviolet (UV) radiation from sun exposure. The most commonly identified mutations occur in the BRAF and NRAS genes. These mutations lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation and survival, disrupting normal cell regulatory mechanisms.
At this localized stage, the cancer cells are still restrained to the epidermis. They show no evidence of spread to the dermis or beyond. However, the presence of these atypical cells is indicative of an ongoing pathological process that, if left untreated, may lead to invasive melanoma.
Diagnosis of Melanoma In Situ
Diagnosing melanoma in situ is a critical aspect of the overall management of this type of skin cancer. This stage of melanoma is defined as being confined entirely to the epidermis, which makes early detection vital. When accurately diagnosed, the prognosis is generally favorable, and this underscores the importance of an effective diagnostic process.
Melanoma in situ often presents with distinct characteristics that require careful evaluation by healthcare professionals. Recognizing atypical moles or lesions during routine skin examinations is paramount. The correct identification and diagnosis can save lives, making it essential for both patients and clinicians to have a comprehensive understanding of the various diagnostic methods.
Clinical Examination
The first step in the diagnosis of melanoma in situ typically involves a systematic clinical examination. During this examination, healthcare providers look for suspicious changes in the skin. The classic signs include asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, a diameter larger than 6 millimeters, and evolving features of existing moles. This method can be successful in identifying concerning lesions, but it should not be the only approach.
Benefits of a thorough clinical examination include:
- Early detection, which is crucial for successful treatment
- Immediate referral to specialists for further evaluation
- Monitoring changes in known moles over time
Standard practice also recommends self-examinations for patients. Educating individuals on how to recognize changes in their skin can support early diagnosis.
Biopsy Techniques
When melanoma in situ is suspected, biopsy techniques are employed to confirm the diagnosis. A biopsy involves taking a sample of the suspicious tissue for histological examination. There are various biopsy methods used in dermatology, each with its specific indications.
Common biopsy techniques include:
- Excisional Biopsy: This method involves removing the entire suspicious lesion along with a margin of surrounding tissue. It is often preferred for its ability to provide not only a diagnosis but also a complete specimen for evaluation.
- Incisional Biopsy: With this technique, only a portion of the lesion is removed for analysis. This method is used when complete excision is not feasible due to the lesion's size or location.
- Shave Biopsy: For superficial lesions, a shave biopsy may be performed where the lesion is shaved off with a surgical blade. This method is quicker and less invasive, but there may be limitations in assessing deeper structures.
Each biopsy technique has its advantages, and healthcare providers must consider the individual patient's situation when choosing the appropriate method. Successful biopsy results lead to a definitive diagnosis, which is vital for planning treatment protocols.
"Timely diagnosis and effective surgical intervention can significantly improve outcomes for melanoma in situ patients."
In summary, the diagnosis of melanoma in situ is a multifaceted process that includes thorough clinical examination and targeted biopsy techniques. Understanding these elements not only benefits healthcare professionals but also empowers patients. This knowledge is crucial in advancing the treatment objectives and improving the chances of successful outcomes.
Surgical Options for Melanoma In Situ
Surgical options are crucial in the management of melanoma in situ. The aim is to remove the cancerous cells effectively while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue. It is important to select an appropriate surgical method based on the tumor’s size, depth, and location. Understanding the benefits and considerations of these surgical approaches can greatly influence patient outcomes.


Excisional Surgery
Excisional surgery is a primary treatment for melanoma in situ. This method involves surgically removing the tumor along with a margin of healthy skin around it. The goal is to ensure complete removal of the melanoma while providing a margin that may minimize the risk of recurrence.
The benefits of excisional surgery include:
- Simplicity: The procedure is straightforward and can often be completed in an outpatient setting.
- Effectiveness: When performed correctly, excisional surgery has a high success rate in removing melanoma in situ.
- Tissue Analysis: Removal of the tissue allows for thorough pathological examination, which helps determine if the cancer has been completely excised.
However, there are considerations to keep in mind:
- Scar Formation: This surgery may lead to noticeable scarring, particularly if the melanoma is in a visible area.
- Need for Follow-Up: Patients require regular monitoring post-surgery to check for recurrence or any new lesions.
Mohs Micrographic Surgery
Mohs micrographic surgery is another effective option for treating melanoma in situ. This method is often used for melanomas located on the face or other cosmetically sensitive areas. Mohs surgery involves the systematic removal of skin cancer layers and immediate microscopic examination of each layer.
The advantages of Mohs micrographic surgery include:
- Maximal Tissue Preservation: Mohs ensures that as much healthy tissue as possible is preserved, which is essential for cosmetic outcomes.
- High Cure Rates: This technique offers high cure rates for melanoma, especially in challenging locations.
- Immediate Results: Patients receive immediate feedback on whether the cancer has been completely removed, reducing the need for additional surgeries.
Despite its benefits, patients should also consider:
- Longer Procedure Time: The process can take longer than standard excisional surgery due to multiple stages of removal and analysis.
- Potential for More Anesthesia: Depending on the extent of the surgery, patients may need more anesthetic, particularly for larger melanomas.
Pre-operative Considerations
Pre-operative considerations are critical in the context of melanoma in situ surgery. These considerations play a pivotal role in the surgical outcome and the overall well-being of the patient. Proper assessment, patient education, and thorough preparation before surgery can significantly influence recovery time, minimize complications, and enhance the effectiveness of the surgical intervention. In this section, we discuss two key components: patient assessment and the informed consent process.
Patient Assessment
A comprehensive patient assessment is essential prior to melanoma in situ surgery. This process involves gathering detailed medical history, conducting physical examinations, and evaluating psychosocial factors that may impact treatment.
- Medical History: It is important to document any previous skin cancers, family history of melanoma, or other relevant medical conditions. Understanding these aspects helps surgeons anticipate potential challenges during the procedure.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the melanoma and surrounding tissue is necessary. This includes assessing the size, depth, and location of the lesion. Based on this assessment, the surgeon can determine the most appropriate surgical technique.
- Psychosocial Factors: Emotional state and support systems can affect a patient’s experience. A discussion about coping mechanisms and mental readiness is essential. Patients should feel empowered and informed about the surgery.
Additionally, pre-operative imaging or further diagnostic tests may be warranted to assess the extent of the disease and to guide surgical strategy.
Informed Consent Process
The informed consent process is a vital legal and ethical step in this journey. It ensures that the patient comprehends all aspects of the surgery, including the risks and benefits.
- Explanation of Procedure: The surgeon should provide a clear outline of the surgical procedure, including how it will be performed and what techniques will be used. This transparency builds trust between the healthcare provider and the patient.
- Risks and Benefits: Discussing potential complications is necessary. Examples include infection, scarring, and recurrence of melanoma. It is equally important to highlight the benefits, such as removing cancerous tissue and reducing further health risks.
- Alternative Options: Patients should be informed about alternative treatment options, including observation or non-surgical approaches. This empowers patients to make knowledgeable decisions about their care.
- Opportunity for Questions: Patients should feel encouraged to ask questions. A supportive environment can alleviate anxiety and promote understanding.
Informed consent is not just a formality; it is a cornerstone of patient autonomy and shared decision-making.
In summary, addressing pre-operative considerations can greatly influence surgical outcomes. Proper patient assessment and a thorough informed consent process pave the way for successful melanoma in situ surgery and enhance the overall patient experience.
Surgical Procedure Overview
The surgical procedure overview is a critical section in understanding the treatment of melanoma in situ. This part outlines the surgical methods utilized, emphasizing their significance in achieving effective patient outcomes. A thorough overview sheds light on the practical aspects of surgery, informs about necessary preparations, and clarifies the procedural steps involved. Knowledge of surgical techniques allows medical professionals to make informed decisions tailored to individual patient needs.
Anesthesia Options
During surgery for melanoma in situ, adequate anesthesia is key to ensuring patient comfort and minimizing pain. Generally, there are two main types of anesthesia used in these procedures:
- Local Anesthesia: It numbs the specific area where the surgery will occur. This option is often suitable for smaller excisions, allowing patients to remain awake while undergoing the procedure.
- General Anesthesia: This is used for more extensive surgical interventions. Under general anesthesia, the patient is completely unconscious and unaware of the procedure.
The choice of anesthesia depends on various factors, including the extent of the melanoma, the patient’s overall health, and the anticipated length of the surgery. Medical professionals must evaluate these aspects carefully to select the best option.
Step-by-Step Surgical Process
Understanding the step-by-step process of melanoma in situ surgery provides clarity on what to expect before going into the procedure. Here’s a concise outline of the surgical process:
- Preoperative Preparation: The surgical team explains the procedure to the patient, addressing any questions or concerns. Patients might be asked to avoid certain medications.
- Anesthesia Administration: The chosen anesthesia is administered to the patient, ensuring they are comfortable and pain-free.
- Surgical excision: The surgeon begins by removing the localized melanoma, followed by a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal. This step is essential to minimize the risk of recurrence.
- Closure of the Wound: After excision, the wound is closed using stitches or adhesive closure strips. The method depends on the size and location of the incision.
- Postoperative Care Initiation: Once surgery is complete, the patient is monitored in a recovery area to ensure they are stable before discharge.
Important Note: Each surgical case may vary significantly. Hence, personalized assessments should dictate the specific techniques and protocols employed.
In summary, the surgical procedure for melanoma in situ involves detailed planning and execution. Following well-defined steps ensures that patients receive the necessary care while maximizing their chances of a successful outcome.
Post-operative Care
Post-operative care is a critical phase in the management of melanoma in situ surgery. It involves a multi-faceted approach to ensure effective recovery and reduce the risks of complications. Understanding the components of post-operative care can lead to improved outcomes for patients. Communication with healthcare providers is essential during this phase. Patients must be educated about what to expect and how to manage their recovery properly.
Immediate Care Following Surgery
After surgery, immediate care focuses on monitoring the patient for any early signs of complications. Healthcare providers typically assess vital signs and observe the surgical site closely. They check for excessive bleeding, signs of infection, or adverse reactions to anesthesia. This ensures any complications can be addressed promptly.
The following steps are common during the immediate care period:
- Ensure the patient is stable and comfortable.
- Apply dressings as required to the surgical site.
- Provide pain management through prescribed medications.
- Instruct the patient on the importance of rest and avoiding strenuous activities in the early recovery phase.
Prompt identification and management of post-surgical complications can greatly enhance recovery and minimize the risk of long-term issues.
Wound Management
Wound management is an essential aspect of post-operative care contributing to faster healing and reduced risk of infections. Proper care of the incision site is vital. Patients should follow specific guidelines provided by their healthcare team, which might include:
- Keeping the area clean and dry.
- Changing bandages as instructed to maintain hygiene.
- Not submerging the wound in water until initialized by a healthcare provider.
- Identifying signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, or discharge.
Managing the wound properly not only aids in recovery but also minimizes the risk of scarring.


Monitoring for Recurrence
Monitoring for recurrence post-surgery is critical in managing melanoma in situ. Regular follow-up visits with healthcare professionals are vital for early detection of any new skin changes or lesions. Patients should be educated about self-examination techniques to monitor their skin effectively. Health care providers often recommend:
- Monthly self-examinations for any new or changing moles.
- Scheduled follow-up appointments for professional skin assessments.
- Awareness of family history and personal risk factors, as these can inform follow-up care frequency.
Long-term monitoring plays an important role in ensuring that any recurrence of melanoma is caught early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Complications and Risks
Understanding complications and risks associated with melanoma in situ surgery is vital. Patients and healthcare providers must be aware of these factors to ensure safe, effective treatment. Risks may not only affect the surgical outcome but can also influence the patient’s overall health and recovery trajectory. Being informed about potential complications empowers patients to ask the right questions, adhere to follow-up protocols, and ultimately foster better health outcomes.
Potential Surgical Complications
Surgical procedures for melanoma in situ come with inherent risks. These complications can vary in severity and impact. Common potential surgical complications include:
- Infection: The surgical site may become infected, requiring antibiotics or even further interventions.
- Hemorrhage: Excessive bleeding is a risk during and post-surgery, which can lead to hematomas.
- Scarring: Every surgical intervention can lead to varying degrees of scarring, which may concern patients cosmetically.
- Anesthesia Reactions: Some patients may experience adverse reactions to anesthesia, affecting their recovery.
- Nerve Damage: Nearby nerves can be inadvertently affected during excision. This can result in numbness or altered sensation in the surgical area.
Regular communication between the surgical team and the patient is crucial. It allows for the identification of any signs of complications early, which is essential for prevention and management.
Long-term Risks of Melanoma
The long-term risks associated with melanoma in situ surgery extend beyond the immediate postoperative period.
- Recurrence: Melanoma can come back, even after successful surgical intervention. Monitoring for signs of recurrence is critical.
- Risk of New Melanomas: Patients with a history of melanoma in situ may be at higher risk for developing new melanoma lesions in other skin areas.
- Psychological Impact: The diagnosis and treatment of melanoma can lead to anxiety or fear of cancer recurrence, affecting patients' quality of life.
- Surveillance: Lifelong dermatological follow-ups are typically recommended. Regular skin checks help detect any early signs of melanoma or other skin diseases.
Important note: Emphasizing education on skin self-examinations can also play a role in decreasing long-term risks by empowering patients to monitor their skin diligently.
In summary, awareness of both potential surgical complications and long-term risks of melanoma can significantly influence the treatment process. By navigating these risks, patients can better prepare and manage their health throughout their recovery journey.
Psychological Impact of Melanoma Surgery
Understanding the psychological impact of melanoma surgery is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. Surgery for melanoma, especially when it involves significant skin excisions, can elicit profound emotional responses. The insights gained from examining these psychological facets can inform pre-operative counseling and post-operative support, leading to improved patient outcomes.
Patients often face a multitude of emotions before and after their melanoma surgery. Fear, anxiety, and uncertainty about the future are common. The diagnosis itself is distressing, compounded by the surgical process and the possibility of recurrence. For many, the emotional trauma can linger long after the physical healing is complete. This makes it necessary to acknowledge and address these emotions, as they can influence recovery and the overall quality of life.
A comprehensive approach to managing the psychological impact involves education, empathy, and support mechanisms. Educating patients about what to expect from surgery, recovery, and potential complications can reduce anxiety. Moreover, incorporating support systems that provide emotional and mental health resources can make a significant difference.
"Emotional adjustment is as important as physical recovery in managing melanoma surgery outcomes."
Emotional Responses to Diagnosis
The diagnosis of melanoma in situ often leads to an emotional rollercoaster for patients. Initial feelings may include disbelief or denial, as many view melanoma as a serious health threat. Following this, guilt or shame may arise, particularly related to lifestyle choices or perceived failures in sun protection.
Patients may also experience anger, which could stem from feelings of helplessness in controlling their health. This emotional spectrum can seem overwhelming, but it is essential to understand that these responses are normal. Acknowledging these feelings can foster an environment where patients feel supported and validated.
Support groups and therapy can play a vital role in helping patients process these emotions. Therefore, ensuring access to mental health professionals is highly beneficial.
Support Mechanisms Available
Various support mechanisms are available to address the psychological impact of melanoma surgery. These include:
- Counseling Services: Professional counseling can help patients navigate their feelings and develop coping strategies post-surgery.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have experienced similar diagnoses can provide comfort and a sense of community. Online platforms, such as those found on Reddit or Facebook, often host these groups.
- Educational Resources: Providing educational materials about what to expect during the recovery process can help minimize anxiety.
- Family and Friends: Encouragement from loved ones is invaluable. Open communication about feelings can foster a supportive atmosphere.
Rehabilitation and Follow-up
Rehabilitation and follow-up are crucial components in the treatment of melanoma in situ. After surgical intervention, patients need to focus not only on healing physically but also on adjusting to their life post-surgery. The follow-up process is more than just an appointment; it provides an opportunity for healthcare providers to monitor recovery, prevent recurrence, and support physical and emotional health.
Importance of Follow-up Visits
Follow-up visits are an essential part of the management of melanoma in situ. They allow healthcare professionals to evaluate the surgical site for any signs of complications or recurrence. Regular monitoring helps to identify any abnormal changes early, which is key to effective management. It also provides a platform for discussing any concerns the patient might have regarding their recovery or new symptoms that may arise.
During follow-up visits, doctors might perform a physical examination and recommend skin checks for new or changing lesions. Furthermore, the psychological aspect of dealing with a skin cancer diagnosis can also be addressed during these visits. It can be beneficial for patients to discuss their emotional health, as this is often neglected in the physical recovery process.
- Ensure to schedule follow-ups as advised.
- Keep records of physical changes and emotional aspects post-surgery.
Lifestyle Adjustments Post-Surgery
After surgery, making certain lifestyle adjustments is necessary to aid recovery and reduce the risk of recurrence. These changes can vary from adjusting skin care routines to making dietary changes that bolster the immune system. Some key adjustments include:
- Sun Protection: After surgical treatment, the skin can be particularly sensitive. Patients should use sunscreen with high SPF and wear protective clothing when outdoors.
- Regular Monitoring Self-Exams: Getting into the habit of regularly examining the skin for any new spots or changes can be a lifesaver. This proactive approach encourages early detection of any potential issues.
- Balanced Diet: Incorporating a diet rich in antioxidants may help in recovery. Foods such as berries, nuts, and leafy greens can support overall health and improve immunity.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in gentle exercise can promote circulation and overall physical health. However, it is essential to consult with a physician about the type and duration of activities suitable post-surgery.
Adopting these lifestyle changes not only aids recovery but also instills a sense of control and empowerment in patients after such a significant health event.
Through attention to rehabilitation and committed adherence to follow-up appointments and lifestyle changes, patients can enhance their recovery journey and optimize long-term outcomes.
Patient Education and Resources
Patient education is a foundational element in the journey of individuals dealing with melanoma in situ. It encompasses disseminating crucial information regarding the diagnosis, treatment options, and post-operative care. Educating patients allows them to take an active role in their health decisions, fostering a sense of empowerment. Understanding their condition enables better adherence to treatment protocols and mitigates anxiety surrounding the surgical process.
Educational Materials for Patients
Educational materials serve as essential tools in enhancing patients' grasp of their situation. They can include brochures, pamphlets, and digital content that provide clear, concise information about melanoma in situ. These resources often cover various aspects such as:
- Understanding Melanoma In Situ: Definitions and disease progression.
- Treatment Options: Detailed descriptions of surgical procedures including excisional surgery and Mohs micrographic surgery.
- Post-operative Care: Guidelines regarding wound care and monitoring for recurrence.
The availability of these materials can significantly benefit patients by:


- Improving Knowledge: Clear information helps demystify complex medical terms.
- Enhancing Treatment Compliance: When patients understand their treatment plan, they are more likely to follow through effectively.
- Facilitating Informed Decision-Making: Patients can engage meaningfully with healthcare providers about their options.
Online Support Communities
In today’s digital age, online support communities have become invaluable resources for patients facing melanoma in situ. These platforms allow individuals to connect with others experiencing similar challenges, providing both emotional and practical support.
Key aspects of these communities include:
- Connection with Peers: Patients can share experiences and coping strategies, reducing feelings of isolation.
- Access to Resources: Many groups provide shared knowledge about additional educational materials, events, and current research.
- Emotional Support: Members can offer encouragement and perspective, which is crucial during difficult times.
These platforms, such as those on Reddit or Facebook, enhance patient education by fostering open conversations about personal experiences, thus promoting a communal understanding of melanoma in situ challenges. Active participation in these communities can lead to increased patient confidence and a better coping strategies.
"Knowledge is power, and empowering patients through education is crucial in melanoma management."
In summary, effective patient education and the leverage of support resources make a significant impact on treatment outcomes. The aim is always to ensure patients feel informed, supported, and equipped for the journey ahead after a melanoma in situ diagnosis.
Current Research and Advances
Current research and advances in the field of melanoma in situ surgery are crucial. This area not only highlights innovative techniques but also embraces emerging therapies that can significantly impact patient outcomes. Medical professionals and researchers are increasingly focusing on these developments to enhance surgical precision and post-operative care, improving the overall management of melanoma.
Innovative Surgical Techniques
The emergence of innovative surgical techniques has shifted the landscape of melanoma treatment. Notably, techniques such as Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy (SLNB) have gained prominence. This procedure helps identify the first lymph node that cancer cells are likely to spread to, guiding further treatment.
Another technique gaining traction is fluorescence-guided surgery. It employs fluorescent dyes to enhance tumor visualization, allowing for more accurate excisions. These advanced methods provide several benefits:
- Increased Precision: Surgeons can remove more targeted areas, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
- Reduced Recurrence Rates: Improved accuracy in excision lowers the chances of melanoma returning post-surgery.
- Faster Recovery: Less invasive techniques can contribute to quicker healing times.
Furthermore, the integration of robotic assistance in surgery has begun to be explored. Robotic systems can enhance dexterity and control, potentially leading to better surgical outcomes. Overall, these innovations underscore the ongoing evolution in surgical techniques.
Emerging Therapies and Treatments
In addition to surgical advancements, there is an increasing focus on emerging therapies that complement melanoma in situ surgery. Immunotherapy, for example, is transforming treatment protocols. This approach utilizes the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Key developments include:
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: Medications like Pembrolizumab or Nivolumab help the immune system recognize and destroy cancerous cells more effectively.
- Adjuvant Therapies: These treatments are administered after surgery to eliminate remaining cancer cells, reducing the risk of recurrence.
Targeted therapies also play a vital role in the management of melanoma. Drugs designed to target specific genetic mutations can help treat patients more effectively.
The advancements in both surgical methods and therapy options provide an integrated framework for managing melanoma. As this research progresses, the implications for clinical practice are profound, enhancing the quality of patient care.
"Innovation in surgical techniques and emerging therapies mark a promising era for melanoma treatment, shifting the paradigm towards more effective, personalized care."
Future Directions in Melanoma Management
The future of melanoma management stands at a crucial juncture. As we delve deeper into the nuances surrounding melanoma in situ, it is essential to recognize the evolving landscape of surgical practices and treatment methodologies. The significance of this topic can’t be overstated. Advancements in surgical techniques, enhanced patient care protocols, and the integration of modern technology are redefining how we approach melanoma treatment. These changes hold promise for improving patient outcomes and reducing the recurrence rates of this skin cancer.
Trends in Surgical Practices
Surgical practices for melanoma in situ are progressively evolving, influenced by ongoing research and clinical insights. Notably, there is a trend towards minimally invasive approaches. There is a growing preference for techniques that promote quicker recovery and less disruption to the surrounding tissue. For instance, less invasive procedures like Mohs micrographic surgery facilitate the precise removal of cancerous cells while preserving healthy skin, which can be critical for aesthetic reasons.
Key elements defining the trends in surgical practices include:
- Increased use of surgical robots: Robotic-assisted surgery allows for enhanced precision and control during procedures. This can lead to reduced scarring and shorter recovery times.
- Patient-centered practices: Surgeons increasingly emphasize tailored treatment plans based on individual patient needs and the specific characteristics of the melanoma.
- Changing guidelines: The latest clinical guidelines are pushing the boundaries of traditional care paths, allowing for more personalized and effective surgical interventions.
These trends not only improve surgical outcomes but also enhance the overall patient experience by mitigating anxiety associated with surgery and recovery.
Integration of Technology in Treatment
Technological integration in melanoma treatment is a game-changer. As the field expands, the use of technologies like artificial intelligence and telemedicine is becoming more prevalent. These innovations contribute to better diagnostic accuracy and more effective patient management.
Considerations include:
- AI and machine learning in diagnostics: Algorithms are increasingly utilized to analyze skin lesions, improving early detection rates for melanoma in situ. This can lead to quicker interventions and better prognoses.
- Telemedicine for follow-up care: Remote consultations allow healthcare providers to monitor patients post-surgery without the need for physical visits. This is particularly beneficial for individuals in remote areas or those with mobility challenges.
- Wearable health technologies: Devices capable of monitoring skin changes provide patients and clinicians with valuable data, facilitating timely interventions.
The introduction of technology in melanoma management not only streamlines care but also empowers patients to take an active role in their health monitoring.
Closure
The conclusion serves as a pivotal component in understanding the surgical approach to melanoma in situ. This section synthesizes the essential insights garnered throughout the article, providing clarity on several key aspects. First, it reaffirms the significance of timely and effective surgical intervention. The earlier melanoma is diagnosed and treated, the better the prognosis for the patient. This highlights the role of education and awareness both for patients and healthcare providers.
In this article, we also emphasized the variety of surgical techniques available for melanoma in situ, such as excisional surgery and Mohs micrographic surgery. Each method has unique advantages and considerations. Recognizing these differences helps patients make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Furthermore, the post-operative care, including wound management and monitoring for recurrence, is crucial for achieving optimal recovery. Patients must be aware of potential signs of complications and the importance of follow-up consultations. This comprehensive view reinforces that melanoma treatment extends beyond the operating room.
Overall, the conclusion encapsulates the necessity of a well-rounded approach to melanoma in situ surgery. Healthcare professionals play a vital role in guiding patients through diagnosis, surgical choices, and recovery strategies, optimizing long-term outcomes for individuals facing this condition.
Summary of Key Points
- Melanoma in situ is a critical stage of skin cancer confined to the epidermis, requiring urgent intervention.
- Timely surgical procedures are essential for treatment effectiveness.
- Excisional surgery and Mohs micrographic surgery are the primary techniques, each with specific benefits and risks.
- Post-operative care should focus on wound management, monitoring, and regular follow-ups to ensure no recurrence occurs.
- Patient education is vital to empower effective decision-making regarding treatment and recovery processes.
Final Thoughts on Melanoma Surgery
The journey through melanoma surgery, particularly for melanoma in situ, encompasses various phases that are interconnected. From understanding the diagnosis to selecting the right surgical technique, each step is critical. Patients should actively participate in their treatment decisions, facilitated by thorough discussions with their healthcare providers.
As research advances, new surgical techniques and therapies continue to emerge, shaping the landscape of melanoma management. It remains important for patients and healthcare professionals alike to stay informed about innovations in the field.
By understanding the implications of their choices and the potential outcomes associated with each surgical intervention, patients can foster a proactive approach to their health. Melanoma surgery is not just about removing cancer but also ensuring a better quality of life post-treatment.
"Awareness and proactive measures are essential in reducing the impact of melanoma and improving patient outcomes."
Through collaboration and continued education, we can elevate the quality of care and outcomes for those affected by melanoma in situ.















