D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride: Insights and Applications

Intro
D-glucosamine hydrochloride, a derivative of the naturally occurring amino sugar glucosamine, has gained attention in the realm of joint health and osteoarthritis management. Many have turned to this compound in hopes of finding relief from the discomfort often associated with these conditions. While the sheer mention of glucosamine may evoke thoughts of dietary supplements and wellness brochures, a deeper dive into its chemistry, biological effects, and therapeutic applications reveals a landscape far more intricate and layered than one might assume. This narrative will unravel the complexities surrounding D-glucosamine hydrochloride, offering insights that are crucial for those engaged in health and life sciences.
Research Context
Background Information
D-glucosamine hydrochloride has become a pivotal element in the discussion surrounding joint health. It is often classified within the category of nutraceuticals, primarily sought after by those suffering from joint wear and tear or inflammatory conditions. Traditionally, glucosamine is produced in the body from glucose and the amino acid glutamine and plays a key role in the formation and repair of cartilage—the resilient connective tissue in joints. However, as age sets in or injuries occur, the natural production of glucosamine diminishes, leading to issues like osteoarthritis.
Importance of the Study
The significance of studying D-glucosamine hydrochloride cannot be overstated. As the average lifespan extends, coupled with an increasingly active demographic, understanding how this compound impacts joint health becomes crucial. Researchers and healthcare professionals are actively investigating its properties to ascertain not only its efficacy but also how it might fit into comprehensive treatment regimens. The ongoing exploration into its pharmacological mechanisms provides a window through which the clinical community can not only better treat patients but also enhance overall quality of life.
Discussion
Interpretation of Results
In recent studies, D-glucosamine hydrochloride has displayed potential benefits, particularly in terms of pain relief and improved function in patients with osteoarthritis. For example, some findings suggest a noticeable reduction in pain scores among individuals taking this supplement as compared to placebo groups. The effects have been varied depending on the dosage and duration of treatment, which further complicates the narrative as various factors can influence outcomes. Such findings beckon a more robust analysis of protocols and recommendations for use.
Comparison with Previous Research
When contextualizing contemporary findings against historical research, several trends emerge. Previous meta-analyses have suggested that glucosamine's effectiveness may be limited, often drawing skepticism regarding its utility. However, newer investigations reveal promising directions—estimating varying responsiveness based on genetic predispositions and other health conditions. This raises important considerations about personalization in treatment and suggests that a one-size-fits-all approach may no longer suffice.
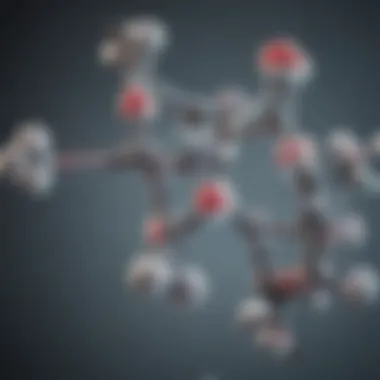
Chemical Structure of D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride
Understanding the chemical structure of D-glucosamine hydrochloride is foundational for appreciating its role in biochemistry and pharmacology. This section elaborates on its intricate molecular composition and the synthesis processes that enable its production and utilization in health sciences.
Molecular Composition
D-glucosamine hydrochloride is a derivative of glucose and is classified as an amino sugar. Its molecular formula is C₆H₁₃ClN₄O₆S, reflecting a blend of various elements defined in its structure. The core composition consists of:
- Carbon (C): Six carbon atoms constitute the backbone of the molecule, giving it the complexity typical of polysaccharides.
- Hydrogen (H): Thirteen hydrogen atoms are bonded to carbon and nitrogen, influencing the solubility and reactivity of the compound.
- Chlorine (Cl): The presence of one chlorine atom as part of the hydrochloride variant introduces significant implications for its stability and excipient properties.
- Nitrogen (N): One nitrogen atom classifies this compound as an amino sugar, crucial for its biological activity as it participates in the formation of glycosaminoglycans.
- Oxygen (O): Six oxygen atoms are involved in multiple hydroxyl groups, affecting how the compound interacts with other biological molecules and signaling pathways.
The structural representation can be visualized as a six-membered ring, similar to glucose, but with an amino group replacing the hydroxyl group on the second carbon. This shift aids in promoting biological processes such as cartilage formation, particularly relevant in the context of joint health. Also, the hydrochloride form ensures enhanced solubility, making it more bioavailable when consumed.
Synthesis Processes
D-glucosamine hydrochloride can be synthesized from chitin, which is found in the exoskeletons of crustaceans. This natural source employs a complex process involving deacetylation, whereby acetyl groups are removed to produce pure D-glucosamine. The steps typically involve:
- Chitin Extraction: Chitin is extracted from crustacean shells, usually by treating with alkaline solutions to break down proteins and minerals.
- Deacetylation: Chitin is then treated with strong alkaline solutions, often sodium hydroxide, to yield D-glucosamine. This process converts the acetylated form of chitin into the amine form.
- Neutralization: After obtaining D-glucosamine, the product is reacted with hydrochloric acid to produce D-glucosamine hydrochloride, which stabilizes the compound for various applications.
The significance of understanding these processes lies in their implications for industrial applications. Pharmaceutical manufacturers can take advantage of biological sources and synthetic methods to ensure a consistent and high-quality product. Various studies often cite this compound in the context of its use in supplements for joint health; the methods of production further emphasize the importance of sourcing and purity in clinical outcomes.
"The careful synthesis and composition of D-glucosamine hydrochloride significantly influence its therapeutic efficacy in clinical practices, making knowledge of its structure crucial for health professionals."
In summary, the molecule's rich composition and the intricacies of its synthesis processes are integral for anyone diving into its biological and therapeutic roles, particularly regarding developments in joint health and osteoarthritis management.
Biological Mechanisms
Understanding the biological mechanisms behind D-glucosamine hydrochloride is crucial for grasping its implications in joint health and cartilage formation. This section provides insight into how this compound functions within the body, emphasizing its metabolism and key roles in maintaining healthy joint structures. With increasing interest in the management of osteoarthritis, recognizing these mechanisms aids both healthcare professionals and researchers in applying knowledge to therapeutic practices.
Metabolism in the Body
When consumed, D-glucosamine hydrochloride undergoes a series of metabolic processes. It is primarily absorbed in the small intestine, entering the bloodstream and getting transported to various tissues. A notable aspect of its metabolism is the conversion into glucosamine-6-phosphate, which serves as a precursor for glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans. These molecules are essential components of cartilage and other connective tissues.
- Absorption Process: After ingestion, glucosamine hydrochloride is swiftly hydrolyzed, allowing its active form to enter the circulatory system, where it can exert its effects.
- Tissue Utilization: The bioavailability of this compound means that it can readily reach chondrocytes—cells found in cartilage—stimulating them to produce cartilage matrix components. This powerful action underscores its therapeutic potential in conditions like osteoarthritis.
It’s worth noting that individual metabolic rates can vary based on factors such as age, weight, and overall health.
Role in Cartilage Formation

D-glucosamine plays a significant role in cartilage formation, contributing to the synthesis of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans. These substances provide cartilage its structural integrity and lubrication, essential for joint function. The following points summarize its pivotal functions:
- Cartilage Matrix Production: D-glucosamine encourages chondrocytes to enhance the production of the cartilage matrix. This action is critical for maintaining cartilage health, especially in conditions where cartilage degradation occurs.
- Modulating Inflammation: There is emerging evidence suggesting that D-glucosamine may help in mitigating inflammatory responses in joints, thus alleviating some symptoms associated with osteoarthritis. By dampening such responses, it aids in preserving cartilage.
"The harmony of cartilage structure and function is not just vital but essential for the resilience of joints over time."
In summary, recognizing how D-glucosamine hydrochloride is metabolized and its role in cartilage formation provides valuable insights into its potential applications in joint health. These biological mechanisms highlight not just the compound’s therapeutic significance but also set the stage for future research and clinical practices.
Therapeutic Applications in Medicine
Understanding the therapeutic applications of D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride is crucial for anyone engaged in health sciences or clinical practice. This section will address its significance in treating joint-related conditions, particularly osteoarthritis, a common ailment affecting millions globally. By examining D-Glucosamine's recognized roles and its evolving status in the medical landscape, we can appreciate its potential contributions to patient care and treatment strategies.
Use in Osteoarthritis Management
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most prevalent form of arthritis, characterized by the degradation of joint cartilage and underlying bone. D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride is often hailed as a cornerstone in managing OA, primarily due to its perceived benefits in cartilage synthesis and repair.
Research indicates that D-Glucosamine may help alleviate the symptoms of OA, such as pain and stiffness. The compound is believed to favorably influence cartilage metabolism, which can lead to reduced inflammation and improved joint function. Many healthcare practitioners recommend D-Glucosamine supplements, especially for individuals seeking alternatives to traditional pain relief medications.
It’s important to consider dosage and timing when integrating D-Glucosamine into treatment regimens. Typically, healthcare professionals suggest starting with a dosage of 1500 mg per day, divided into two or three doses. This method might maximize absorption and minimize the potential for gastrointestinal upset. As always, a patient’s health history should be reviewed to tailor the approach to individual needs, optimizing outcomes effective and safely.
Potential Benefits for Joint Health
Beyond osteoarthritis, D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride offers broader implications for joint health, making it a topic of keen interest for researchers and practitioners alike. While most discussions center around OA, ongoing studies also explore its role in supporting overall joint function in various conditions.
Some potential benefits of D-Glucosamine include:
- Anti-inflammatory properties: It might help reduce joint inflammation, contributing to a better quality of life for those with chronic pain.
- Suppression of cartilage breakdown: D-Glucosamine may help protect against the degradation of cartilage, potentially slowing down the progression of joint disorders.
- Combination with other therapies: Evidence suggests that combining D-Glucosamine with other nutraceuticals, such as chondroitin sulfate, could enhance its benefits, providing a comprehensive approach to joint health.
"D-Glucosamine's role as a supportive tool in joint health extends beyond simplicity; it embodies a nuanced interaction with bodily processes, presenting a valuable addition to traditional therapeutic practices."
Scientific Research and Studies
D-Glucosamine hydrochloride has garnered a considerable amount of attention in recent years, particularly regarding its implications for joint health and its therapeutic potential in osteoarthritis management. Understanding the importance of scientific research and studies surrounding this compound is crucial, as it provides insights into its mechanisms, effects, and overall relevance in the field of health sciences. Investigation into D-glucosamine does not only reveal its biological actions but also opens up discussions on the methodologies of research that inform best practices in medicinal use.
Research contributes significantly to validating claims about the benefits of D-glucosamine. Without empirical studies, individual anecdotes about its effectiveness fall flat. Thus, the impact of these studies extends beyond individual health benefits and speaks to broader medical applications. They help practitioners, researchers, and policymakers grasp the compound's significance and its potential to improve patient care.
Clinical Trials Overview
Clinical trials serve as the backbone of evidence-based medicine, and D-glucosamine hydrochloride is no exception. Numerous trials have been conducted to analyze its effects on osteoarthritis symptoms, particularly focusing on joint pain and functionality. These clinical investigations often involve diverse groups, ranging from patients with mild discomfort to those afflicted with severe joint degeneration.
A key component of these trials is the randomized control design, where participants are assigned to either a treatment or placebo group. This methodology ensures that the results are not biased by external factors, allowing for more accurate conclusions about the efficacy of D-glucosamine. For many patients, these trials often mean the difference between continuing with traditional pain management strategies or exploring new avenues for relief. In addition to pain relief, the trials also scrutinize how D-glucosamine affects the progression of joint degeneration over time.
Efficacy and Outcomes
When looking at the efficacy of D-glucosamine hydrochloride, the results from clinical trials are mixed yet informative. Some studies indicate significant reductions in joint pain and improved mobility in patients taking D-glucosamine compared to those who received a placebo. Specifically, research has found that older adults suffering from knee osteoarthritis reported a notable decrease in pain levels after several weeks of treatment.
However, not all outcomes have shown uniform success. Some trials revealed minimal to no difference compared to a placebo, which raises questions about the compound's effectiveness for certain individuals.
The variability in findings could be attributed to factors like:
- Differences in dosages used.
- Variations in patient demographics.
- The stage of joint degeneration at the start of treatment.
"D-glucosamine’s efficacy is not just about the compound itself, but also about how each patient interacts with it within the complexities of their health status."
Such nuances highlight the need for further studies that can dissect these variables to improve treatment protocols. As research continues, attention to how each aspect of D-glucosamine treatment affects patient outcomes can guide future work, potentially leading to more personalized approaches in joint health management.
Controversies Surrounding D-Glucosamine
In recent years, the use of D-glucosamine hydrochloride has generated considerable debate among health professionals, researchers, and consumers alike. As more studies emerge, there is a twisting path of opinions and conflicting research results that complicate the narrative surrounding this supplement. Understanding the controversies is pivotal not just for those considering its use but also for medical practitioners guiding patients in their health journeys. Highlighting these uncertainties ensures critical insights into the supplement's potential benefits as well as its limitations.
Divergent Research Findings
Research surrounding D-glucosamine is a patchwork of perspectives, with some studies presenting promising results while others reveal a less optimistic picture. On one hand, some clinical trials have found that D-glucosamine can significantly reduce symptoms of osteoarthritis, leading to better mobility and less pain for patients. These studies often cite the compound's role in cartilage formation and joint health.


Conversely, there are rigorous studies that challenge these assertions. For instance, some meta-analyses report minimal to no clinical significance, indicating that while glucosamine might offer slight symptom relief, the evidence is not robust enough to recommend it as a primary treatment for joint degeneration. This divide leaves consumers grappling with whom to trust, as marketing often touts glucosamine’s efficacy without addressing conflicting scientific literature.
"The lack of a consensus in scientific findings leaves a sea of uncertainty for patients seeking effective treatments for joint pain."
Analyzing multiple studies could benefit from considering factors such as dosage, sample size, and the duration of treatments, as these elements can heavily influence outcomes. Moreover, the divergence often arises from varying methodologies used in research, making it challenging to conclusively declare D-glucosamine as either a miracle supplement or an ineffective placebo.
Expert Opinions
When it comes to D-glucosamine, expert opinions are as varied as the research they base their views on. Some healthcare professionals advocate for its use in conjunction with other treatments for osteoarthritis, arguing that the supplement might serve as a valuable adjunct therapy. They often emphasize the importance of understanding individual patient responses, suggesting a trial-and-error approach may be beneficial in finding what works best for a particular patient.
In contrast, other experts remain highly skeptical. They caution against jumping on the glucosamine bandwagon, suggesting there's insufficient evidence to warrant its widespread use. These professionals stress the significance of relying on well-founded medical treatments over supplements, especially when the efficacy is not strongly supported by rigorous scientific data.
The marketplace is also filled with testimonials and anecdotes from individuals who claim significant improvement with glucosamine, which can complicate matters even further.
Ultimately, the conversation surrounding D-glucosamine should be approached with a balanced perspective, considering both positive anecdotal experiences and the caution of seasoned researchers. As the dialogue continues, clear communication about the existing evidence and limitations remains essential for both consumers and health practitioners.
Potential Side Effects and Risks
When considering the use of D-glucosamine hydrochloride, it’s crucial to understand potential side effects and risks involved. As beneficial as it may be for joint health, no supplement is without its drawbacks. This section aims at exploring common adverse reactions and notable contraindications.
Common Adverse Reactions
While many people tolerate D-glucosamine without any issues, some may experience adverse reactions. Here are a few that have been reported:
- Gastrointestinal discomfort: Users often report feelings of nausea, diarrhea, or bloating. These issues can vary in intensity, often depending on the dosage taken. In some cases, lowering the dose or taking the supplement with food may alleviate symptoms.
- Allergic reactions: Though rare, some individuals have had allergic reactions, which can manifest as skin rashes, itching, or hives. Allergies can sometimes be tricky; those with shellfish allergies might want to exercise caution, as glucosamine is derived from shellfish in some formulations.
- Fatigue and drowsiness: Another reported effect is unusual tiredness. This can interfere with daily activities or work, leading to decreased productivity, notably in those who operate machinery or drive.
- Headaches: There's evidence mentioned by some users experiencing headaches. This could stem from various factors, including changes in diet or even the body's response to the supplement.
It’s worth noting that most adverse effects are mild, but awareness is essential. If any of these symptoms persist or worsen, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
Contraindications
Certain individuals should steer clear of D-glucosamine supplements, emphasizing the need for prudent use. Consider the following contraindications:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women: Safety during pregnancy and lactation hasn’t been established. Therefore, it's best to avoid the component unless specifically advised by a healthcare provider.
- Individuals with diabetes: Some studies suggest that glucosamine might affect insulin sensitivity. Thus, it’s crucial for diabetics to monitor their blood sugar closely and consult their doctor before starting the supplement.
- Those on anticoagulant therapy: Glucosamine may interfere with blood-thinning medications, raising the risk of bruising or bleeding. It is advisable to consult a physician for a proper assessment and guidance.
- People with shellfish allergies: As mentioned earlier, some glucosamine formulations are made from shellfish. Those with allergies should seek alternatives that are not shellfish-derived, ensuring safety.
In summary, while D-glucosamine hydrochloride presents various benefits, attention to potential side effects and contraindications should not be overlooked. Being informed helps users make educated decisions about their joint health strategies.
Always discuss with a healthcare provider before beginning any new supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking other medications.
By understanding these nuances, individuals can better navigate their options in joint health.
Marketing and Availability
The discussion surrounding D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride wouldn’t be complete without delving into its marketing and availability in the health and wellness industry. Understanding how this supplement is presented in the market impacts both its accessibility and the perceptions held by consumers regarding its efficacy and utilitarian value.
In recent years, there has been an uptick in awareness regarding joint health and osteoarthritis, driving the demand for products containing D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride. Not only do various manufacturers advertise it as a preventive measure for joint deterioration, but they also tout it as a remedy for existing joint ailments. This overlap in marketing strategies has fueled some confusion amongst consumers about the supplement's real benefits. With words like "natural" and "support for mobility" thrown around, potential buyers may find it challenging to parse fact from fiction.
Commercial Forms and Dosages
D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride is available in several forms, making it versatile for different user preferences. The most common forms include:
- Capsules: Convenient for those on the go, these are easy to take and manage dosage.
- Powders: Some users prefer a powder form to mix into smoothies or drinks, allowing for customized dosages.
- Liquid Solutions: For individuals who struggle with swallowing pills, liquid forms offer an accessible alternative.
- Chewables: These are particularly appealing to younger audiences or individuals who find it easier to consume flavored supplements.
Each commercial form usually comes with its recommended dosages, which often range from 1,500 mg to 3,000 mg per day, depending on usage and desired effects. It is crucial for consumers to consult healthcare professionals to establish appropriate dosages tailored to their unique health profiles.
Regulatory Oversight
When it comes to the regulatory framework surrounding D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride, it's vital to note that the supplement industry operates under different rules than prescribed medications. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) does not formally approve dietary supplements before they hit the shelves. Instead, it is the responsibility of manufacturers to ensure that their products are safe and accurately labeled. This situation leads to a mixed bag of quality and reliability across various brands.
The lack of stringent oversight raises important considerations:
- Consumers need to be aware that the market may include products lacking in efficacy or quality.
- Certifications from third-party organizations (like the United States Pharmacopeia) can offer some security, ensuring that the supplement passes certain standards of quality and purity.
- Monitoring the product’s sourcing and manufacturing processes is equally essential, as transparency provides insight into what one is putting into their body.
Finally, one could argue that better regulatory frameworks would improve consumer trust and safety. Understanding the nuances of the supplement's marketing and availability can significantly aid consumers in making well-informed choices about their joint health.


"The importance of understanding product marketing and regulatory practices cannot be overstated, especially in the supplement sector, where consumer health is on the line."
Through these lenses—commercial forms, dosages, and regulatory positions—one can see just how pivotal marketing and availability are in shaping the narrative around D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride.
Alternative Perspectives on Joint Health
The discourse around joint health often emphasizes singular treatments or well-known supplements like D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride. However, establishing a more comprehensive view can enhance understanding and treatment effectiveness. Exploring alternative perspectives on joint health entails examining diverse approaches and concepts that extend beyond conventional methodologies. This section aims to illuminate the holistic nature of joint health, which includes synergistic benefits of various practices, diverse opinions from experts, and the relevance of nutritional interventions.
Holistic Approaches
Holistic health is all about seeing the big picture. It advocates for treating the whole person, rather than merely alleviating specific symptoms. In the context of joint health, this means considering lifestyle, mental well-being, physical activity, and nutrition. When combining various strategies, patients may find themselves on a path to improved joint function and overall health.
- Mind-Body Connection: Techniques such as yoga and tai chi can help harmonize body movements with mental focus, potentially reducing pain and increasing flexibility. Not only does this training strengthen joints, but it can also help in managing stress, which might have an indirect effect on joint health.
- Physical Activity: Engaging in low-impact exercises is crucial. Activities like swimming or cycling can promote mobility without overstraining joints. Regular movement keeps joints lubricated, maintaining their functionality.
- Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can exacerbate joint pain. Incorporating stress management practices, such as meditation or deep breathing, can yield positive outcomes.
This holistic lens on joint health encourages individuals to modify their lifestyle, promoting a balanced approach toward well-being, which is often neglected in traditional prescriptions.
Nutritional Supplements
When diving into nutritional supplements, it’s imperative to recognize their potential in complementing treatments for joint health. While D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride has gained attention for its role in supporting joint function, other supplements can also play a significant role.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish oil, these compounds possess anti-inflammatory properties that could help reduce joint pain and stiffness.
- Turmeric: This spice contains curcumin, which has been studied for its ability to help relieve inflammation. It may provide a natural alternative for those tired of over-the-counter medications.
- Chondroitin Sulfate: Often found alongside glucosamine, chondroitin helps maintain cartilage integrity and could enhance joint health further.
- Collagen: A crucial protein for cartilage repair, collagen supplementation might also foster joint health and mitigate wear and tear associated with aging.
Incorporating these supplements into one’s diet, preferably with professional guidance, can complement the effects of D-Glucosamine Hydrochloride. The additive effect of these nutrients may create a more robust framework for managing joint health issues.
"A synergistic approach, combining different treatments and supplements, may yield better results than relying on one solution alone."
Through these alternative perspectives, the importance of a well-rounded approach to joint health becomes evident. Rather than merely treating problems as they arise, embracing various strategies may lead to long-term benefits that foster greater well-being.
Future Directions in Research
As the landscape of joint health research continues to evolve, the exploration of D-glucosamine hydrochloride reveals several future directions worthy of attention. This section aims to clarify the significance of advanced research in this area, specifically referencing emerging studies and innovations in treatment protocols which are critical for improving patient outcomes and refining therapeutic applications.
Emerging Studies
The investigation surrounding D-glucosamine hydrochloride has been expanding, particularly as new methodologies and technologies emerge. A variety of studies are underway, examining not only its efficacy in managing osteoarthritis but also its broader applications.
Studies focusing on the mechanistic pathways of D-glucosamine can shed light on how this compound interacts at the cellular level. Recent trials have examined its role in anti-inflammatory responses and cartilage repair mechanisms, leading to a more refined understanding of its therapeutic potential. Researchers are also looking at its combination with other drugs to enhance effects, particularly in multimodal pain management strategies.
Moreover, observations suggest that the bioavailability and absorption rates of glucosamine can vary widely among individuals due to age, dietary habits, and health conditions. As a result, there’s a push towards personalized medicine; studies are emerging to identify biomarkers that might predict how well a patient could respond to glucosamine supplementation.
"To truly harness the benefits of D-glucosamine, we must embrace a tailored approach that takes into account individual patient variability."
- Health Research Journal
Innovations in Treatment Protocols
The future search of treatment protocols involving D-glucosamine hydrochloride should prioritize integrative approaches that combine pharmaceutical and non-pharmaceutical strategies. Given the evolving understanding of pain biology, there's ongoing research into how glucosamine might be effectively incorporated into holistic treatment frameworks alongside physiotherapy, exercise regimens, and dietary adjustments.
For instance, integrating D-glucosamine into treatment plans for conditions beyond osteoarthritis could unlock its potential for improving joint health and function in other populations. Researchers are investigating its role in musculoskeletal disorders, offering hope that it could provide support for aging populations or even athletes facing joint stresses.
- Treatment Innovations include:
- Combining glucosamine with anti-inflammatory agents to enhance efficacy.
- Exploring various formulations (e.g., injections, oral supplements).
- Studying the effects of glucosamine adjunct therapy in post-operative recovery.
Collaboration among disciplines—rheumatology, nutrition, and physiotherapy—can expedite innovation, ensuring that treatment protocols are evidence-based and adaptable. As we look toward these evolving strategies, it's essential to remain committed to rigorous research methodologies to validate the efficacy and safety of these approaches.
Anticipating the landscape of joint health treatment means adapting our strategies and embracing the complexities that lie ahead with D-glucosamine hydrochloride at the forefront. By keeping a keen eye on emerging studies and fostering innovations in treatment protocols, we can significantly impact future therapeutic practices.
Ending
In summarizing the complexities surrounding D-glucosamine hydrochloride, this article underscores its crucial role in joint health and osteoarthritis management. With an intricate blend of biological understanding and clinical applications, it's evident that this compound isn't just a footnote in health discussions; instead, it's a key player. Notably, the various findings presented throughout the sections reveal both the promising potential and the nuanced challenges associated with D-glucosamine.
Summary of Findings
- Chemical Properties: D-glucosamine hydrochloride is not just a supplement; it’s a chemical compound with a well-defined molecular structure that plays multiple roles in the body’s metabolism.
- Biological Mechanisms: The metabolism of this compound underpins its therapeutic attributes, particularly in supporting cartilage health and aiding in joint lubrication.
- Therapeutic Benefits: A wealth of research suggests that D-glucosamine can provide relief for those suffering from osteoarthritis, although the effects may vary from person to person.
- Controversial Perspectives: Amidst the scientific acclaim, there are dissenting voices and critical studies that call for caution, urging further investigation into its efficacy and safety.
- Practical Implications: The compelling evidence makes it imperative for healthcare professionals to consider D-glucosamine in treatment plans while remaining aware of its limitations and varying responses.
Implications for Practice
- Personalized Approach: Understanding the biological variability among patients is fundamental. Not every individual will respond to D-glucosamine in the same way, thus necessitating a tailored treatment protocol that factors in personal health conditions and needs.
- Integration in Treatment: It's essential for practitioners to integrate D-glucosamine thoughtfully with other treatments. This approach could optimize outcomes, especially for patients dealing with chronic joint issues.
- Continuous Education: Healthcare providers should stay abreast of ongoing research to utilize D-glucosamine effectively. Workshops, seminars, and recent literature can support practitioners in providing evidence-based recommendations.
In summary, D-glucosamine hydrochloride presents both opportunities and challenges. Its implications are profound, affecting not just the clinical approach to osteoarthritis but also enhancing overall understanding of joint health. Thus, professionals must remain vigilant and informed as they navigate this evolving landscape.















