Azacitidine's Impact on Skin: Side Effects Explained

Intro
This article explores the skin-related side effects of azacitidine, a medication primarily used in cancer treatment. As with many therapies, understanding the impact on patient well-being encompasses more than just the medication's primary effects. Azacitidine operates through mechanisms that can influence skin integrity, leading to various dermatological reactions. The complexity of these side effects warrants closer examination, as they can significantly affect a patient's quality of life during treatment.
Patients and healthcare providers need to recognize the potential for skin problems when initiating treatment with azacitidine. This understanding fosters proactive management strategies that can mitigate discomfort and enhance the overall treatment experience. Here, we will detail the findings from recent studies, clinical insights, and case reports that spotlight the significance of monitoring dermatological reactions in individuals undergoing azacitidine therapy.
Research Context
Background Information
Azacitidine, also known by the brand name Vidaza, is a nucleoside analog that is particularly effective in treating hematologic malignancies such as myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Its mechanism promotes the reactivation of tumor suppressor genes by inhibiting DNA methyltransferase. Although it works effectively against cancer, azacitidine is not without its adverse effects, particularly concerning the skin.
Skin reactions can arise during treatment, ranging from mild rashes to more severe manifestations that require clinical intervention. These side effects can be distressing and may alter treatment adherence, thus impacting treatment outcomes.
Importance of the Study
Investigating skin side effects associated with azacitidine is crucial for multiple reasons. Firstly, comprehensive knowledge aids healthcare providers in recognizing and addressing these reactions promptly. Secondly, awareness of the correlation between skin side effects and patient outcomes can lead to improved management strategies tailored to individual needs. Understanding the importance of dermatological monitoring enables better overall patient care.
Furthermore, this article contributes to the existing body of literature by synthesizing recent research findings, ultimately reinforcing the significance of skin health in the oncological treatment spectrum. By examining the interplay between azacitidine and dermatological health, we hope to provide clarity and actionable insights for both clinicians and patients.
"Monitoring skin reactions is an integral part of cancer treatment, especially with medications like azacitidine that have known dermatological side effects."
Discussion
Interpretation of Results
Data show a variety of skin effects tied to azacitidine treatment. Common reactions include erythema, pruritus, and even severe skin toxicity in some patients. Understanding these issues helps clinicians set realistic expectations for patients and encourages discussions about ongoing skin care during therapy.
Comparison with Previous Research
Previous studies have emphasized the need for dermatological assessments in patients undergoing various cancer therapies. Azacitidine's specific profile in regards to skin manifestations can be differentiated from those observed with other treatments such as chemotherapy or targeted therapies. These distinctions are pivotal in shaping treatment plans and in providing tailored patient education.
Preamble to Azacitidine
Azacitidine is a medication with significant relevance in the treatment of specific malignancies, particularly myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia. Understanding azacitidine’s role is crucial for medical professionals and researchers, as it is often considered a linchpin in managing these conditions. This section will elucidate how azacitidine functions within the body and its appropriate usage, paving the way to investigate its potential side effects, particularly those that affect the skin.
Mechanism of Action
Azacitidine works primarily as a hypomethylating agent. This means it inhibits DNA methylation, a process that can lead to the activation of tumor suppressor genes. By reversing abnormal methylation patterns, it aims to restore normal cellular function in cancerous cells. This action can slow down or halt the progression of cancer by inducing cell differentiation and apoptosis in malignant cells. Given its unique mechanism, it is imperative to understand not only how azacitidine helps treat cancer but also its broader implications for patient health, especially concerning dermatological reactions.
Indications for Use
Azacitidine is indicated for the treatment of several hematological malignancies. These conditions primarily include:
- Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS): A group of disorders caused by poorly formed or dysfunctional blood cells.
- Acute myeloid leukemia (AML): A cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow.
- Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML): A type of cancer that has characteristics of both leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes.
These indications represent significant clinical applications of azacitidine, highlighting its relevance in oncology. As more patients receive this treatment, understanding the nuances of its side effects is essential for all stakeholders in patient care.
Understanding Skin Reactions
In the context of azacitidine treatment, understanding skin reactions is vital for both patients and healthcare providers. These skin reactions can serve as indicators of how a patient's body is responding to the drug. Such knowledge assists in early detection of potential issues, allowing for timely intervention and management.
Skin reactions not only affect the appearance of the skin but can also influence a patient's psychological well-being. Higher awareness of these reactions supports better compliance with treatment regimens, as patients are more informed about what to expect. Moreover, understanding the varying types of skin reactions provides a clearer framework for clinicians to tailor their treatment approaches, enhancing patient care.
Common Types of Skin Reactions
Rashes
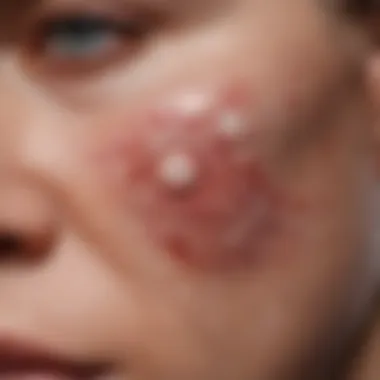
Rashes are among the most prevalent skin reactions observed in patients undergoing azacitidine treatment. They typically present as red or inflamed patches, often accompanied by discomfort. The significance of rashes lies in their ability to reveal underlying immune responses triggered by the medication.
The key characteristic of rashes is their variable presentation, which might range from mild irritation to extensive dermatitis. This variability allows for an insightful discussion on how different patients may experience different symptoms. Understanding this aspect makes rashes a critical focus in this examination.
A unique feature of rashes is their potential to lead to more severe complications if left unaddressed. They can become infected or lead to further systemic issues, necessitating active monitoring and management strategies.


Itching
Itching, or pruritus, is another common skin symptom associated with azacitidine. It often accompanies rashes but can also occur independently, which makes it an important focus in patient care. The discomfort associated with itching can significantly affect the quality of life for patients, leading to sleep disturbances and anxiety.
The distinctive characteristic of itching is how it often signals an inflammatory process occurring in the skin. Understanding the mechanisms behind itching can lead to prudent patient management and intervention strategies. Its inclusion is relevant in our ongoing discussion about improving patient care while using azacitidine.
One advantage of addressing itching includes the possibility of reducing unnecessary distress among patients. Effective management strategies can enhance overall patient satisfaction and adherence to treatment.
Dryness
Skin dryness is frequently reported as a side effect of azacitidine, leading to a range of discomforts. Dryness manifests as scaling, flaking, and a tight sensation on the skin. It can aggravate existing skin conditions, making its management essential for patient comfort.
The significance of skin dryness is marked by its commonality across various demographics. Its pervasive nature makes it a relatable issue for many patients receiving treatment. The inclusion of dryness in this article allows for a well-rounded discussion of skin reactions.
A notable aspect of dryness is its impact on the skin barrier function. Compromised barrier integrity may lead to increased susceptibility to infections and further skin concerns. Thus, understanding and addressing dryness is paramount for maintaining skin health in azacitidine-treated patients.
Mechanisms Behind Skin Side Effects
The skin reactions associated with azacitidine stem from complex biological processes. The underlying mechanisms include immune modulation, altered skin barrier function, and systemic effects facilitated by the medication.
Through better understanding of these mechanisms, healthcare providers can optimize treatment plans and mitigate negative effects. A detailed examination can lead to informed discussions on adjusting dosages or incorporating supportive therapies that can enhance skin health during treatment.
Recognizing these mechanisms also makes it possible to initiate patient education programs that empower individuals to manage their skin health proactively.
Prevalence of Skin Side Effects in Patients
The prevalence of skin side effects in patients undergoing azacitidine treatment is critical for understanding the overall impact of this medication. Skin reactions can significantly affect a patient's quality of life, leading to distress and possible discontinuation of therapy. Establishing how common these side effects are can inform clinicians and patients about what to expect during treatment, enabling better management strategies. Furthermore, understanding the prevalence helps in designing future research as well as adapting treatment protocols accordingly.
Clinical Studies Review
Study Samples
When looking at clinical studies, it is paramount to consider the study samples utilized. The usual approach includes examining a range of patients with different demographics and health backgrounds. The diverse characteristics of these samples provide a well-rounded view of how azacitidine impacts various groups. Studies often include participants diagnosed with specific types of cancers, allowing for clear conclusions on azacitidine's effects on skin in these populations.
The key benefit of varied study samples is to ensure the results are applicable across different patient scenarios. However, one unique feature might also be the breeding of specific conditions within sample groups which can skew results.
Methods of Assessment
The methods used to evaluate skin side effects during clinical studies are crucial. These might include basic reporting of symptoms by patients, dermatologist evaluations, or structured assessments like the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events. Each method has its strengths; for example, structured assessment tends to provide quantitative data that help in comparing results across studies.
The primary advantage of using established assessment criteria is consistency. However, a potential disadvantage is that subjective experiences might be overlooked, thus potentially missing nuances in patient experiences during treatment.
Comparative Analysis
Azacitidine vs Other Treatments
When comparing azacitidine with other treatment options, such as decitabine or traditional chemotherapy, it’s essential to focus on the skin side effects each treatment may provoke. Azacitidine often shows a more favorable profile for skin-related side effects compared to some chemotherapy regimes, which may cause more pronounced dermatitis and rashes. This comparative analysis can guide clinicians in selecting appropriate therapy based on the tolerability profiles for patients.
Moreover, the unique aspect of azacitidine is its targeted action against malignant cells, which may help prevent extensive skin damage, providing a less toxic alternative.
Long-term vs Short-term Effects
Understanding the difference between long-term and short-term effects of azacitidine on skin reactions is vital. Short-term reactions might include acute erythema and itching shortly after administration, while long-term exposure could potentially lead to chronic skin conditions such as eczema or persistent dryness. This assessment helps tailor ongoing monitoring strategies for patients receiving this treatment.
A significant advantage of analyzing these effects is that it may help in early detection and intervention strategies, improving patient outcomes. However, the complexities of chronic reactions can lead to mismanagement if not adequately monitored.
The ongoing documentation of skin side effects is essential to optimize treatment protocols and enhance patient quality of life.
Symptoms of Skin Reactions
Understanding the symptoms of skin reactions related to azacitidine treatment is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. These reactions can vary in severity and directly affect the quality of life for individuals undergoing cancer therapy. Early recognition and management of these symptoms can help prevent further complications and a deterioration of skin health. Moreover, a deep understanding of these symptoms allows for better discussion between patients and clinicians, ensuring that appropriate care strategies can be employed effectively.
Identifying skin symptoms helps in personalizing treatment plans, making adjustments if necessary, and enhancing the overall patient experience. These factors contribute to better health outcomes and greater adherence to treatment regimens.


Identifying Dermatitis
Dermatitis is among the most prevalent skin reactions experienced by patients treated with azacitidine. It can manifest in several forms, including contact dermatitis, which results from skin exposure to irritants or allergens. Symptoms typically include redness, swelling, and itching of the affected area.
Recognizing this condition early is important. Patients should be educated on how to examine their skin regularly and report any unusual changes. Management often involves supportive care along with medications to reduce inflammation and discomfort. Identifying dermatitis promptly can prevent it from progressing to more severe conditions, helping to maintain skin integrity throughout treatment.
Recognizing Severe Cases
In treatment settings, it is critical to differentiate between mild irritation and severe skin reactions. Severe cases can present with more alarming symptoms that require immediate attention.
Symptoms of Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to azacitidine are noteworthy, as they can escalate quickly. Key characteristics often include extensive redness, hives, or a rash that appears suddenly. Symptoms may also include swelling around the eyes and lips, and in more severe instances, difficulty breathing may occur.
The early recognition of these symptoms is essential. If reported promptly, it may lead to interventions that can minimize complications. Educating patients about these symptoms can be beneficial because they may not always associate new skin reactions with their treatment. The urgency lies in addressing allergic responses swiftly to avoid further health risks and provide appropriate care.
Signs of Infection
Signs of infection are another critical area of focus when discussing skin reactions. Potential symptoms include increased redness, warmth, swelling, and the presence of pus in the affected area. These symptoms may also accompany severe pain or fever.
Recognizing signs of infection is vital for maintaining patient safety and health. If there is a suspicion of infection, immediate medical evaluation is necessary. Delayed treatment can lead to serious complications, which is why educating patients about these signs can empower them in their own care. Knowing what to look for allows for timely intervention, thus reducing potential healthcare burdens.
Overall, a thorough understanding of skin symptoms related to azacitidine therapy is essential. It equips both patients and medical providers with the knowledge needed to act quickly and appropriately, fostering an environment of safety and care.
Management of Skin Side Effects
The management of skin side effects associated with azacitidine treatment is crucial in ensuring patient compliance and overall quality of life. Effective management strategies can significantly mitigate discomfort, promoting better adherence to therapy. Managing these skin reactions becomes not just a clinical challenge, but a necessary part of holistic patient care. It is vital for clinicians to understand both topical and systemic options to alleviate symptoms while minimizing disruption to treatment regimens.
Topical Treatments
Emollients
Emollients are a fundamental part of managing skin conditions. Their primary function is to restore moisture and create a protective barrier on the skin. This characteristic makes them particularly valuable for patients suffering from dryness, which can exacerbate discomfort during azacitidine therapy. A unique feature of emollients is their ability to fill the spaces between skin cells, which helps repair the skin's natural barrier.
The use of emollients has its advantages. They are generally well-tolerated and can be easily incorporated into a patient's daily routine. However, some patients may experience a greasy feeling or a reaction to specific ingredients.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are often utilized to manage inflammation and itching associated with skin reactions. Their anti-inflammatory properties make them an effective choice for individuals experiencing dermatitis due to azacitidine. A key characteristic of corticosteroids is their potency, allowing for quicker relief of symptoms.
The unique feature of corticosteroids is their ability to reduce swelling and redness efficiently. However, long-term use can potentially lead to skin thinning, making it essential for clinicians to balance effectiveness with safety in monitoring patient's response.
Systemic Approaches
Antihistamines
Antihistamines play a vital role in managing allergic reactions and itching. In the context of azacitidine treatment, antihistamines provide relief from the skin irritations that may occur. A significant characteristic of antihistamines is their sedative effect, which can assist patients in getting better rest.
While antihistamines are generally beneficial, they may cause drowsiness or other side effects. This necessitates careful consideration when prescribing, particularly in patients who need to maintain alertness.
Adjusting Azacitidine Dose
Adjusting the dose of azacitidine can be an effective way to manage skin side effects. This approach allows patients to continue receiving treatment while minimizing the severity of reactions. A vital aspect of this method is the importance of individualized care.
The unique feature of this strategy lies in its adaptability. Clinicians can tailor the treatment plan based on the patient's response and symptom severity. However, close monitoring is necessary, as changing the dose could impact the treatment's efficacy.
Patient Quality of Life
Patient quality of life is a critical aspect to consider when examining the effects of azacitidine, especially regarding its skin-related side effects. When patients undergo treatment, they do not only deal with the medical implications of the drug but also the psychological and social impacts that these side effects can cause. Understanding this topic enhances the overall discussion as it links medical outcomes with patient well-being.
Impact of Skin Reactions on Daily Living
Skin reactions, such as rashes and dermatitis, can hinder a patient’s daily life. These issues are not merely cosmetic; they can lead to significant discomfort and distress.


Psychosocial Effects
The psychosocial effects of skin reactions are profound. Often, visible skin symptoms can trigger feelings of embarrassment, anxiety, and depression in individuals. The psychological impact is just as crucial as the physical reactions caused by azacitidine. The key characteristic of these effects is their ability to isolate patients socially. Patients may withdraw from activities they once enjoyed.
This isolation can exacerbate mental health issues, making it essential to address during treatment. These effects are beneficial to highlight in this article as they illustrate the holistic impact of treatment. By acknowledging the unique feature of these psychological concerns, healthcare providers can work towards integrating mental health support into the overall treatment plan.
Their role is significant in managing the treatment experience effectively.
Healthcare Burden
The healthcare burden resulting from skin reactions cannot be ignored. Patients with side effects from azacitidine often require additional medical consultations, therapy, and treatments to manage their skin conditions. This not only increases healthcare costs but also strains healthcare resources.
A key characteristic of this burden is the need for additional components of care, such as dermatology referrals and symptomatic treatments. This adds workload to healthcare providers, making it a relevant point for discussion in our article.
One unique feature of this burden is that it can divert attention from the primary cancer treatment, potentially hindering the overall care pathway. In this way, discussing the healthcare burden foregrounds the importance of a comprehensive treatment strategy that considers all facets of patient care.
Support Strategies
Supporting patients can mitigate the negative effects of skin reactions substantially. Effective strategies involve patient education and caregiver participation.
Patient Education
Patient education empowers individuals to understand their condition and management options better. This key characteristic of education provides patients insight into skin reactions and ways to alleviate discomfort.
It also encourages adherence to treatment; when patients know what to expect, they are likely to manage their experience better. An advantage of patient education is its ability to foster a sense of control among patients, which is crucial for their mental well-being. Conversely, insufficient education can leave patients misinformed, leading to anxiety and ineffective self-care practices.
Caregiver Involvement
Caregiver involvement is another essential component of patient support. Family and friends can help monitor symptoms and provide emotional support. Key characteristic of caregiver involvement is its capacity to foster a network of support that can recognize changes in the patient’s condition and advocate for their needs.
An advantage of active caregiver participation is it enhances communication with healthcare providers, allowing for a tailored approach to specific patient needs. However, caregivers may experience their own burden, sometimes feeling overwhelmed by the responsibilities of supporting someone undergoing treatment for cancer.
Research Gaps and Future Directions
The exploration of azacitidine's skin-related side effects reveals significant research gaps and opportunities for future inquiry. Understanding these gaps is crucial for improving patient outcomes and optimizing therapeutic regimens. As dermatological reactions can greatly impact the quality of life, addressing these areas is vital to enhance overall treatment efficacy. This section evaluates specific elements essential for further research, the benefits of filling these gaps, and important considerations surrounding future directions.
Areas for Further Investigation
Identifying which aspects of skin reactions are under-researched helps target future studies effectively. Some notable areas include:
- Long-term Effects: Existing research often focuses on immediate side effects. There is little information on the long-term dermatological impacts of azacitidine therapy. Investigating how these effects evolve over time can provide valuable insights.
- Genetic Factors: Individual genetic variability may influence reactions to azacitidine. Exploring this can lead to personalized treatment and management approaches tailored to specific patient profiles.
- Comparative Studies: There is a need for more comprehensive studies comparing azacitidine with alternative treatments. This could clarify whether certain skin reactions are unique to azacitidine or common across similar therapies.
By delving into these areas, we can enhance our understanding of how azacitidine affects the skin and improve strategies for management and patient care.
Potential for New Treatments
Identifying gaps in current treatment strategies opens pathways for developing new therapies. As the side effects of azacitidine can be significant, seeking innovative solutions is imperative. Some promising directions include:
- Trial of New Topical Formulations: Researching and developing new formulations aimed at mitigating skin reactions could improve patient quality of life. This includes innovative emollients or anti-inflammatory creams that are specifically designed to alleviate symptoms associated with azacitidine.
- Combination Therapies: Investigating the efficacy of combining azacitidine with other medications might reduce the severity of dermatological effects. Studies that examine synergistic effects could yield beneficial results for patients experiencing skin side effects.
- Monitoring Technologies: Advancements in wearable technology could facilitate real-time monitoring of skin conditions in patients undergoing azacitidine treatment. Utilizing this technology could lead to proactive management strategies, reducing the impact of adverse skin effects.
Researching these potential new treatments can contribute significantly to improving the management of skin side effects associated with azacitidine use.
"Every step taken in uncovering knowledge can illuminate pathways previously unimagined, paving the way for improved patient care and therapeutic outcomes."
With careful attention to these research gaps and future directions, we can foster a deeper understanding of azacitidine's skin effects. This ongoing investigation will ultimately contribute to enhanced patient safety and treatment experiences.
The End
In concluding the examination of azacitidine's skin side effects, it is crucial to recognize the multifaceted impact of these reactions. Understanding the complexity of the skin side effects is essential for both clinicians and patients. Monitoring and managing these effects contributes significantly to patient safety and overall treatment efficacy.
Summarizing Key Findings
The analysis has shown several important aspects:
- Prevalence of Skin Reactions: Various clinical studies indicate that skin side effects occur frequently among patients receiving azacitidine. This prevalence highlights the need for vigilance during treatment.
- Types of Reactions: Common skin issues include rashes, itching, and dryness. Knowledge of these specific reactions assists in identifying potential complications early.
- Management Strategies: Effective management includes both topical and systemic approaches. Strategies like using emollients and corticosteroids are vital for alleviating symptoms and improving quality of life.
- Quality of Life Implications: The burden of skin reactions extends beyond physical discomfort. They can affect psychological well-being and daily activities, warranting comprehensive care strategies.
"Effective management of skin side effects can significantly enhance patients' quality of life during azacitidine treatment."
Recommendations for Clinicians
Clinicians should adopt a proactive approach to managing skin side effects of azacitidine:
- Routine Monitoring: Regular skin assessments should be part of the treatment protocol to identify reactions as they occur.
- Patient Education: Educating patients about potential skin side effects can enhance their awareness and encourage timely reporting of symptoms.
- Personalized Care Plans: Tailoring management strategies to suit individual patient needs can improve outcomes. This includes considering patient history, skin type, and previous reactions.
- Collaboration with Dermatology: For complex cases, involving dermatology specialists can provide advanced management options that may not be readily available in standard care settings.
By implementing these strategies, clinicians can address the challenges presented by skin side effects, ultimately leading to improved patient adherence and outcomes.















